Writing Fair Multiple-Choice Exams that Challenge Students
advertisement

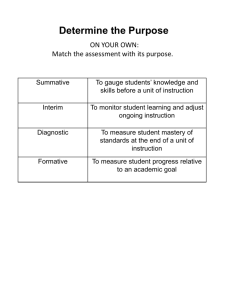
Keith Thiede, College of Education Andy Goodman, Center for Teaching & Learning Introductions Goals Agree on higher order thinking skills Consider iterative process of test construction Consider role of item analysis Explore means of preparing students for the test Examine 2 recipes for multiple choice test construction ◦ Write at least one multiple choice test question for one of your courses ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Bloom’s taxonomy (see handouts) Differences in higher and lower order thinking skills Grid game ◦ information presented is factual or conceptual and represent different levels of thinking ◦ Place the objective in the appropriate block ◦ Not all spaces will be filled Easier to write higher order thinking skills when original objective was higher order Which one of the following objectives requires students to engage in higher-level cognitive behavior? Distractor Answer Distractor Distractor A. Recite the alphabet B. Compare two books by the same author C. Identify the parts of the body D. List the three basic types of rocks Stem Alternatives Expect to revise items several times. Simple item analysis can inform this process: ◦ Examine performance on individual items (90/10 rule) ◦ Look at how well distractors worked ◦ Examine performance of top and bottom students Students expectations about tests affect many things: ◦ How they prepare for a test ◦ Their perceptions of the fairness of a test Recipe 1 Consider your learning objective (e.g., application) Align instruction with objective (give students examples and practice applying concept) Align assessment with objective (provide a new situation to assess whether students can apply what they have learned anew) ◦ Scenario ◦ Graph/Data Mrs. Liu’s students completed research papers on life in colonial times. The students worked on their papers for several weeks and turned in their final versions at the end of the marking period. Mrs. Liu evaluated the papers and used the scores she assigned to help determine the students’ report card grades for that marking period. This is an example of what type of assessment? A. formative B. objective C. summative D. standardized Another Example. Directions: Below is a list of flaws often found in the stems of multiple-choice items. For each of the multiple-choice items that follow, decide whether the item stem has any flaws. Use the following symbols to indicate your response: A if the stem contains no flaws B if the stem doesn’t sufficientlyset the problem C if the stem contains a clue to the right answer D if the stem is negatively stated, and the negative is not highlighted E if the stem contains unnecessary, irrelevantwords Each of these symbols can be used more than one time, or not at all. Write your response on the blank line before the item. Each correctly answered item is worth one point. ____ 1. In Africa A. mining diamonds is an i mportant industry.(keyed as the correct response) B. there are many tropical rain forests. C. camel caravans carry trade goods. Recipe 2 – Turning essay questions into multiple choice questions Consider what you want your students to be able to describe/do What are the essential elements you want to see in the answer Turn at least one of those essential elements into the correct answer Consider less or non-essential elements that might be part of an essay response Turn those into the distractors There were several Generative Approach suggestions presented in class for teaching melody (using Bruner’s learning theory). A)What are some of the important aspects to employ when planning a melody lesson for 1st graders? B) Melody has many sub-concepts. Which aspects of melody do you attempt to teach first, second, etc.? Why? Jerome Bruner’s learning theory could best be applied to a music setting in which of the following scenarios? A)Students begin to develop an understanding of pitch by using sol-fege hand signs. Ks learn only sol and mi, 1st grade adds la, 2nd grade adds low do, etc. B) Students begin to develop an understanding of rhythm by walking to and tapping a steady beat in K, using bars that show different lengths in 1st & 2nd grades, and transitioning to standard notation in 3rd. C) Students learn pitch & matching by hearing & echoing a teacher. This begins in K and continues until all children can match pitch accurately. Around 3rd grade they learn a song by rote, then by note. Check out this website for test construction: http://jonathan.mueller.faculty.noctrl.edu/to olbox/tests/morethanfacts.htm Take 10 minutes to write one or two higher order multiple choice test questions and answers Share with tablemates ◦ Your questions ◦ Thought process you used to create the question/responses Testing isn’t easy Application or analysis are the easier higher order thinking skills to assess in multiple choice Goal of testing is to figure out what students know or can do