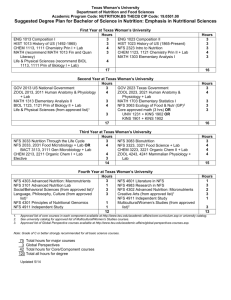
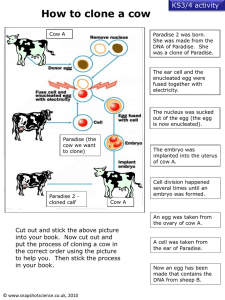
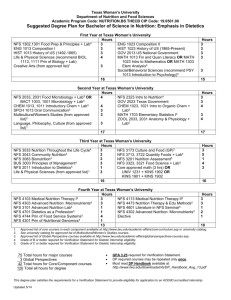
Clonedb - New Zealand Oracle Users Group
advertisement

Clonedb: The quick and easy cloning
solution you never knew you had.
Tim Hall
Oracle ACE Director
Oracle ACE of the Year 2006
OakTable Network
OCP DBA (7, 8, 8i, 9i, 10g, 11g)
OCP Advanced PL/SQL Developer
Oracle Database: SQL Certified Expert
http://www.oracle-base.com
Books
Oracle PL/SQL Tuning
Oracle Job Scheduling
http://www.oracle-base.com
Clonedb: The quick and easy cloning
solution you never knew you had.
• What is a clone?
• Why clone databases?
• How do we clone databases?
• What is Clonedb?
• Demo of Clonedb
• Considerations
http://www.oracle-base.com
What is a Clone?
• An exact copy of the original.
http://www.oracle-base.com
Why Clone Databases?
• Set up new databases as copies of existing ones.
• Data refresh for development and test environments
from production.
• Test backup & recovery.
• Create standby databases.
• Recover lost data or objects
(where flashback is not
appropriate).
http://www.oracle-base.com
How do we Clone Databases?
• There are already several methods for cloning
databases including:
–
–
–
–
Manually copy files and recreate the database.
RMAN DUPLICATE - active database (11g).
RMAN DUPLICATE - backup.
3rd Party solutions.
• All require copying or restoring files
to new location requiring:
– Additional disk space.
– Time to perform the copy.
• Clonedb makes cloning quicker and saves space.
http://www.oracle-base.com
What is Clonedb?
• In 11.1 Oracle added the Direct NFS Client to the
database.
• The 11.2.0.2 patch set introduced Clonedb
functionality, built on top of Direct NFS.
• Clonedb uses Copy-On-Write (COW)
technology for clones.
http://www.oracle-base.com
Copy-On-Write (COW)
Clone
Database
NFS
C.O.W.
Files
Clone
Database
NFS
C.O.W.
Files
Datafile
Image
Copies
• Clones use read-only image copies of datafiles as
source.
• Only modified blocks are written to NFS location.
http://www.oracle-base.com
What is Clonedb? (continued)
• Clonedb saves space when you have multiple clones
as they can all reference the same source files.
• One-time server setup, then repeated
cloning is super-quick.
• Only documented in
My Oracle Support (MOS)
Note 1210656.1
http://www.oracle-base.com
Demo
(cleanup.sql)
http://www.oracle-base.com
NFS Server Setup
• Create a directory to hold the copy-on-write files.
# mkdir -p /u01/nfs-share
• Append the share into the “/etc/exports” file.
/u01/nfs-share
*(rw,sync,no_wdelay,insecure,
insecure_locks,no_root_squash)
• Make sure the NFS service is turned on.
# chkconfig nfs on
# service nfs restart
http://www.oracle-base.com
Production Backup
• Make an image copy backup of the database. The
copy can be placed on a share (CIFS/NFS) or copied
to the local file system of the server running the
clone.
configure controlfile autobackup off;
sql 'alter database begin backup';
run {
set nocfau;
backup as copy database
format ’/u01/backups/prod/%U’;
}
sql 'alter database end backup';
(backup.sh)
http://www.oracle-base.com
Copy Production PFILE
• Take a copy of the production PFILE by running the
following command as the SYS user.
(create_pfile.sh)
CREATE PFILE='/u01/backups/prod/initTEST.ora' FROM SPFILE;
• Edit the PFILE, changing all
references to the original SID
and database name.
http://www.oracle-base.com
Clonedb Server Setup
• Turn on Direct NFS for the ORACLE_HOME on the
clonedb server.
(dnfs.sh)
$ cd $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/lib
$ make -f ins_rdbms.mk dnfs_on
• Make the necessary directories
for the NFS mount and to
support the instance.
(directories.sh)
http://www.oracle-base.com
NFS Mount
• Add the NFS mount to the “/etc/fstab” file, along with
any other necessary shares.
nas1:/u01/nfs-share /u01/copy-on-write
nfs rw,bg,hard,nointr,tcp,vers=3,timeo=600,
rsize=32768,wsize=32768,actimeo=0 0 0
• Mount the copy-on-write location.
# mount /u01/copy-on-write
http://www.oracle-base.com
Clone the database
• Set the required environment variables and run the
“clone.pl” script.
(create_clone_script.sh)
• Review the contents of the
generated files.
• Run the files to create the clone.
(create_clone.sh)
http://www.oracle-base.com
Clone the database
• If you did hot backup you may need to recover
database.
SQL> RECOVER DATABASE USING BACKUP CONTROLFILE UNTIL CANCEL;
SQL> ALTER DATABASE OPEN RESETLOGS;
• Make sure the TEMP tablespace
has been handled properly.
(manage_temp.sql)
• Check the database.
(datafiles.sql)
http://www.oracle-base.com
Considerations - Performance
• Copy-On-Write location is NFS. Is that an issue for
you?
• If a cloned database is to be used
for performance testing, do you
really want a different storage
technology in the mix?
• Possible performance
improvements on the horizon?
http://www.oracle-base.com
Considerations - Space Savings
• Over time more changed blocks will be written to
NFS location, so space savings will reduce.
• Only works with image copies.
If you don’t use image copy
backups how much space are you
really saving?
http://www.oracle-base.com
Considerations - Others
• Very little documentation.
• Very new.
http://www.oracle-base.com
Where would I use it?
• For short-lived clones used for functional, not
performance testing.
• To test backups.
• To recover lost objects.
http://www.oracle-base.com
Where would I NOT use it?
• Setting up long-term clones.
• For clones used for performance testing.
• For setting up a standby database.
http://www.oracle-base.com
Summary
• Very quick cloning.
• Potential for big space savings.
• Need to be on at least 11.2.0.2.
• Need to use NFS for COW location.
http://www.oracle-base.com
The End…
• Download slides and example code at:
http://www.oracle-base.com/workshops
• Article:
http://www.oracle-base.com/articles/11g/Clonedb_11gR2.php
http://www.oracle-base.com