Total Quality Management
advertisement

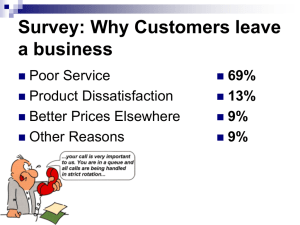
Total Quality Management Presented by C. Christopher Lee Associate Professor of Management Lee (2012): Critical Issues on TQM 1. Customer & Quality 2. Quality Measurements 3. Process Improvement 4. 3 σ (sigma), 4 σ, 5 σ, 6 σ 5. Continuous Improvement 6. Quality & Profitability 7. Total Commitment Customer & Quality • • • • • • The first step of TQM is to define the quality. Customers set an expectation for a product/service. When the expectation is met, customers are satisfied. When customers are satisfied, they validate the quality of the product/service. Therefore, Quality = Customer Satisfaction Review Question (RQ): Who defines the quality? Why? 3 Quality Measurements • • • • • • • After defining the quality for a product/service, the next step is to quantify the quality. A manager should form a team including workers, quality specialist. The manager should lead the team to determine a proper measurement for each process of a product/service; A quality goal can become a measurable number. The quality goal is now set scientifically. Workers will collect the data for the measurement, process & analyze the data, and improve the process. RQ: Why does TQM quantify the quality? RQ: Why do Workers have to be involved in quantifying 4 the quality (planning)? Product Control vs. Process Control • Product Control = Quality Control (old): • Before TQM, we implemented quality control by checking the defect rate of finished goods. This is product control. • This approach does NOT improve the quality. • When you check the quality of finished goods, damages were already done. • Summary: Product control is not TQM. • Reality Check: Still many business organizations conduct “quality control” approach, and think they are implementing TQM. • RQ: Why doesn’t Quality Control improve the quality actually? Product Control vs. Process Control (continued) • • • Process Control = Process Improvement, Quality Improvement, TQM (new): TQM asks you to check the quality in each process of a whole business operation. • If a process shows low quality, you must stop the whole operation, and everyone must solve the particular process immediately. • By improving each process, the whole operation (total quality) is improved, and the quality of the fished good is improved. Summary: OLD NEW Product Control Process Control Quality Control Quality Improvement - TQM RQ: Why is “quality improvement” better than “quality control”? Striving for 6 σ • • SPC: Statistical Process Control 3 σ : Less than 3 defects per 1000 • • 4 σ : Less than 3 defects per 10,000 • • • Contender for Deming Prize 6 σ : Less than 3 defects per 1,000,000 • • • Leader in the industry Contender for Malcom Baldridge Award 5 σ : Less than 3 defects per 100,000 • • Industry standard, Supply chain management World Leader Motorola (early 90s); Toyota (1965-early 2000s) RQ: Why did Toyota lose the 6-sigma reputation in 2000s? Continuous Improvement • OLD: If it is not broken, don’t fix it. NEW: Even if you achieved a quality goal, never stop improving the process. TQM = Continuous improvement = Never-ending process If you stop improving, a competitor will take over your territory soon. To simply survive, you need to continuously improve the quality. 3σ 4σ 5σ 6σ • RQ: Why is TQM a never-ending process? • • • • • 8 Relationship b/w Quality & Profitability REVENUE: 1. Words of Mouth: » » » » 1. Lower WIP: Higher Quality Higher Satisfaction Worlds of Mouth Higher Sales » » » » 2. Higher Price: » » » » Quality Higher Quality Less Defects Less WIP Less Production Cost 2. Lower Returns: Higher Quality Higher Perception Higher Price Higher Revenue Revenue COST: » » » » & Cost Higher Quality Less Defects Less Returns Less Operations Cost Profit !!! Interlinking Quality and Profitability Performance RQ: What is the relationship b/w quality & profitability? Total Commitment • Time & Cost: Improving a process takes a lot of resources (time & cost). Imagine a business operation that involves more than 100 processes. • Long-Term Project: Therefore, TQM must be a longterm project. • Total Quality: Every process in the organization must get involved in quality improvement. • Top Management Support: Top management must commit fully to this TQM project, otherwise the TQM will fail miserably. Without support of CEO/President of a firm, TQM will never be implemented successfully. • RQ: Why does TQM fail without total commitment & full support by top management?