File - Mrs. Glazebrook
advertisement

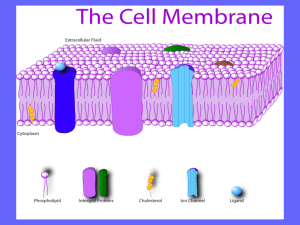
Catalyst 1. What are the 3 parts of the Cell Theory? The smallest… All life is made… All cells come… 2. What is the function of the: Cell membrane Ribosomes Cytoplasm Today’s Objectives SWBAT explain the purpose of the plasma membrane and selective permeability. SWBAT describe the structure of a phospholipid. SWBAT explain how the arrangement of phospholipids lead to the formation of a lipid bilayer SWBAT identify the various components of the plasma membrane Coffee Filter Intro 2) Iodine bag set up 3) Plasma Membrane Lecture 4) Oil/Water demo during notes HW: plasma membrane coloring 1) copyright cmassengale 4 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma or cell membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell 5 Why do houses need walls? Protect it from the environment Decide what can come in and go out Coffee Filter Demo Plasma Membrane The plasma membrane is the flexible outer layer of cells. (inside of cell wall if present) Has three main jobs: Separate cells from the outside 2. Protect cells from the environment 3. Decides what can enter (or exit) the cell 1. Selective permeability: the ability that allows some molecules to pass into the cell while keeping others out >> Check for Understanding How does a window screen show selective permeability? What are membranes made of? Membranes are made up of molecules called phospholipids. Phosphate and glycerol What are membranes made of? Mixes w/ water “HATES” water What are membranes made of? To keep their nonpolar tails away from water, phospholipids form a two-sided layer called a bilayer. Water No Water Water Cell Membrane Polar heads are hydrophilic “water loving” Nonpolar tails are hydrophobic “water fearing” Makes membrane “Selective” in what crosses 14 What are membranes made of? Guided Practice: A-B-C-D Cards For each question, hold up the card for whatever letter you think is correct Question 1 What term means that membranes are made up of two back-to-back layers? a) selective permeability b) non-polar tails c) bilayer d) phophate Question 2 Which part of the diagram below is polar? a) A A b) B c) Both A and B d) Neither A nor B B Question 3 Which part of the diagram below would not mix well with water? a) A A b) B c) Both A and B d) Neither A nor B B Question 4 Which part below will end up in the middle of a bilayer? a) A A b) B c) Both A and B d) Neither A nor B B Question 5 In what types of organisms are cell membranes found? a) prokaryotes b) eukaryotes c) bacteria d) all of the above Question 6 Which of the following are components of a phospholipid? (hold up all that apply) a) fatty acids b) glycerol c) monosaccharides d) phosphate Oil and Water Demo What kinds of items do you think will pass through? For the items that can’t pass through, what can we do to help them get through? Think and answer on your notes 1. In your own words, explain how a pasta strainer shows “selective permeability.” How is this similar to cell membranes? 2. Why do phospholipids form bilayers? 3. How does the oil and water demo relate to the cell membrane? Other Membrane Components Turns out that the cell membrane is NOT this simple: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pfu1DE9PK2w Other Membrane Components There are other parts to the membrane, including cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates Cholesterol: Holding it Together Cholesterol is mixed in with the phospholipids to keep the tails from sticking together. This gives the cells more stability Transport Proteins: The Doors to the Cell Some molecules have trouble crossing the membrane… Why??? Transport proteins help molecules enter or exit the cell. Other Parts: Sending Signals Other proteins and carbohydrates stick out from the cell; they act as signals for other cells to read. The Fluid Mosaic Model The parts of the cell membrane are not held in place; they flow around the cell like boats in water. This is called the fluid mosaic model. Plasma Membrane Worksheet/Coloring