Lipids and Cell Membrane Structure
advertisement

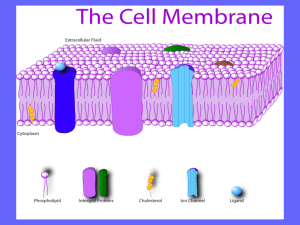
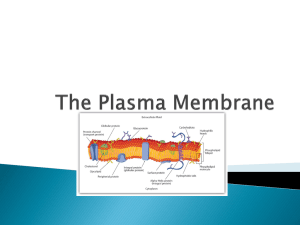
Do Now • Handout 7.2 The Plasma Membrane Before you read handout • Homework – Eukaryotic Cell Structure handout – Organelle quiz on Friday • Know the structures and functions • Be able to label a diagram – Test next Tuesday on Chapter 7 Lipids and Cell Membrane Structure Lipids (a.k.a. Fats) • Lipids are NOT soluble in water. – Lipids are non-polar. • Lipids store large amounts of energy. • The monomers are called fatty acids. • Lipids make up most of the cell membrane. Phospholipids The cell membrane is made of special lipids called phospholipids. Polar heads are hydrophilic – “water loving” Non-polar tails are hydrophobic – “water fearing” The polarity determines the arrangement of the phospholipids. Phospholipids form two layers – called lipid bilayer Polar heads face outward (water outside and inside the cell) Non-polar tails face inward (creates barrier to protect the cell) Cell Membrane Structure • The cell membrane also contains other fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. Cell Membrane Proteins 1. Integral Proteins Proteins that penetrate completely through the membrane (inside) 2. Peripheral Proteins Embedded but not all the way Located on the outside surface and function to help transport different substances into and out of the cell. fluid mosaic model Cell Membrane Functions • Controls what enters and exits the cell. – Selectively Permeable - only lets certain molecules into and out of the cell • Maintains cell’s shape. • Connects each cell to other cells near it. • Can allow movement of the cell – parts can move around each other, called the fluid mosaic model. fluid mosaic model Cell Membrane Model Answers • 1. Phospholipid molecules move freely throughout the membrane in a fluid motion, while the overall structure of the membrane remains unchanged. • 2. Phospholipid has two distinct parts – Polar, hydrophilic head form the inside and outside surfaces of the membrane – 2 Nonpolar, hydrophobic tails form the interior core of the membrane Membrane Model Answers • 3. Selective permeability refers to the fact that the membrane functions as a gatekeeper, monitoring and facilitating the entry and exit of molecules into and out of the cell. • 4. Channels or pumps that actively move waste out of cell and move nutrients into the cell. Closure • Complete The Plasma Membrane handout pg 72-73 • Turn in as you walk out