Poster example
advertisement

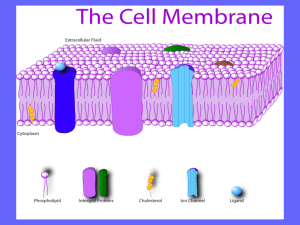
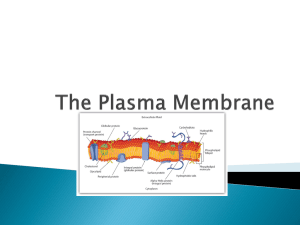
The Effect of Vinegar and Ammonia on the Cell Membrane of a Beet INTRO Membranes are simply phospholipid bilayers and embedded proteins. Phospholipids are two fatty acids that are covalently bonded with a glycerol and a phosphate group. The two nonpolar fatty acids are hydrophobic and the phosphate is hydrophilic. When phospholipids are placed in water, the phosphate “heads” gravitate towards the water with the fatty acid “tails” in between two rows of phosphates, as seen in the picture. Proteins are integrated into this web known as the phospholipid bilayer to perform various other cellular functions. DISCUSSION Student Names Here! OUR EXPERIMENT A Beat, beta vulgaris, contains betacyanin, a red colored pigment, in its cells. When the cell membrane breaks, the betacyanin leaks out of the cell. The goal of our experiment was to break open the membrane using vinegar and ammonia. We hypothesized that vinegar and ammonia would cause betacyanin to leak because the pH level of each chemical would cause the embedded proteins to denature, changing their shape, and break apart the membrane. Chemical Water Acetone (40%) Ethanol (40%) SDS (10%) Ammonia (ph 10) Vinegar (ph 5) RESULTS Betacyanin Extracted .083 .279 .238 .457 .401 .395 *Class average spectrophotometer data PILOT STUDY REFERENCES Hauslein. Cell Membrane. 2008. 1/18/12. MadSci Network: Cell Biology. Madsci.org. 2/1/12. Meyer,Ken. Membrane Lecture: Chapter 5. 1/18/12. Raven, Peter et al.(2008). Biology. 8 ed. page 85-104 Before testing our own chemicals (ammonia and vinegar), we first tested a few others to establish a baseline. Among these were water, SDS, acetone, and ethanol. We learned SDS was the most effective of the chemicals; it worked by disrupting the hydrogen bonds that held the phospholipids together in the bilayer. We also learned that as the concentration of each chemical increased, so did the amount of betacyanin leakage. The data table displays the highest concentration of each chemical that we tested. Our data supports our hypothesis. Vinegar and ammonia were both able to denature the proteins of the membrane and extract betacyanin. One interesting side note of the ammonia test was that instead of the dark red pigment result that we normally obtained, a dark yellow color was extracted. This happened because betacyanin is a natural pigment that contains proteins which were denatured by the ammonia along with the proteins in the membrane. Upon denaturation, the characteristics of the betacyanin proteins changed, which caused the color to change from red to yellow. If we were to further test our hypothesis, we would test more acidic and basic chemicals to see if the amount of betacyanin extracted would increase so as to become as effective as SDS. A procedural error occurred in the water test because theoretically water should not have broken the membrane to release any betacyanin. We believe there was betacyanin on the exterior of the beta vulgaris core to begin due to the removal process braking the membranes of surrounding cells causing betacyanin to leak.