The Plasma Membrane
The Plasma
Membrane
Chapter 7.2
I. The Plasma Membrane Surrounds the
Cell.
Boundary between the cell and its watery environment.
the cell (ex: nutrients
Plasma and waste).
Function: maintain homeostasis (balance) for the cell.
The Plasma Membrane is a selectively permeable membrane.
Allows some molecules to enter and keeps others out
Selective barrier (like a screen door, coffee filter)
II. Structure of the Plasma Membrane
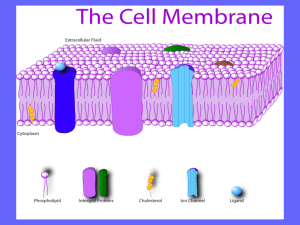
Composed of two layers of phospholipids, called the “phospholipid bilayer”.
Phospholipid molecule
Polar head
(includes phosphate group)
Phospholipids are lipids with a phosphate attached to them.
Nonpolar tails
(fatty acids)
The phosphate head is polar
(hydrophilic = loves water), so it interacts with the watery environment inside the cell and outside the cell.
The fatty acid tails are nonpolar
(hydrophobic = afraid of water) so they avoid water.
Polar heads love water
Non-polar tails hide from water
The Fluid Mosaic Model of the Plasma
Membrane
Fluid because it moves like water http://www.stolaf.edu/people/gi annini/flashanimat/lipids/mem brane fluidity.swf
Mosaic because the proteins make a pattern on the surface.
Carbohydrate chains
Proteins
Transport
Protein
Phospholipids
III. Other parts of the Plasma Membrane
1. Cholesterol – stabilizes the phospholipids and prevents the fatty acid tails from sticking together.
2.
Transport proteins – move needed substances and waste through the plasma membrane, they regulate which molecules enter and leave.
3.
4.
Inner surface proteins – give cell its flexibility
Carbohydrate chains – stick out from the surface of plasma membrane, identifies chemical signals and other cells.
Proteins
Carbohydrate chains
Transport
Protein
Phospholipids