Document
advertisement

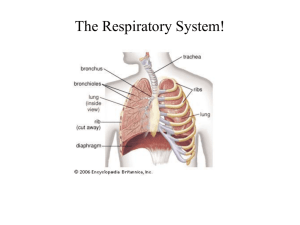
Histology 14 with supplement Much of this is from Histology 14 Liver Respiration Pig liver (20X) Human (20X) • Alternative theory to hepatic systems – Lobule • Classical • Portal – Acinar (grape-like) • • • • • • PV – portal venule A – hepatic artery L – lymphatic duct B – bile duct S – sinusoids Limiting plate Respiratory System • Main functions: – Conducts air in/out – Exchange gasses w/blood – respiration – Includes mechanisms to prevent collapse of conducting tubes • • Bones Cartilage – Two major tube types: 1. Conducting pathway (nasal portion – lungs) 2. Respiration pathway (area of alveolar sacs) Conducting Pathway • Specialized lining of epithelium – “respiratory” epithelium that changes with arborization – Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium • With goblet cells – secrete lots of mucus – Cilia beat in one direction: • Above pharynx – beat downwards • Below pharynx – beat upwards Mucocilary escalator Mucus moved throughout passageway – trap dust Conducting Pathway (cont.) • Blood vessels – warm and moisten air • Trachea (main passageway): – Contains C-shaped rings in adventitia • R,L primary bronchi (enter lungs) • Extrapulmonary• Intrapulmonary- – Same as trachea – Cartilage becomes reduced in bronchi of lungs – Epithelium – begin with pseudostrat ciliated to ciliated columnar • Bronchioles – Epithelium – ciliated cuboidal to non-ciliated simple squamous • Terminal bronchioles • Respiratory bronchioles – start of the respiratory pathway • Decrease in cartilage, glands, goblet cells height of epithelium • Increase in smooth muscle and elastic tissue Cells • Type I pneumocytes – – – – 95% of alveolar surface Highly flattened Simple squamous epithelium Form occluding junctions with one another • Barrier to extracellular fluid into alveolus • Type II pneumocytes – More numerous; only about 5% of alveolar surface – Cuboidal – Dispersed among type I pneumocytes and form occluding junctions with them – Job: provide surfactant – glycoprotein; reduces surface tension (alveolus won’t collapse) • Dust Cell – Small macrophages – Can pass over gas-blood barrier of alveoli Trachea xs Trachea ls • • • • E – epithelium LP – lamina propria SM – submucosa F – fibroelastic tissue Primary bronchus • • • • E – epithelium LP – lamina propria M – smooth muscle G – seromucous glands • C – cartilage • Goblet Cells in epith. Bronchiole • V – vein • M – sm. Muscle • Terminal portion of respiratory tree – – – – – – T – terminal bronchiole R – respiratory bronchiole V – pulmonary vessel AD – alveolar duct AS – alveolar sac A - alveolus Drawings of gas exchange • • • • • Capillaries Lumen of capillary Endothelial cell Lumen of alveolus Pneumocytes