Maniac Magee Literary Elements
advertisement

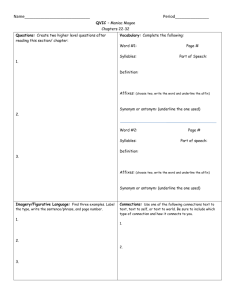
Maniac Magee Literary Elements Maniac Magee Literary Elements Chapters 1 - 5 Sequence of Events The order in which things happen in a story is called the sequence of events. Recognizing what happens first, next, and last in a story will help you understand what you read. Cause and Effect A cause is what makes something happen. The thing that happens is the effect. It’s important to look for cause-and-effect relationships as you read so that you can better understand a story and the characters in it. Characterization A character is a person in a story. Sometimes characters are described directly by the author or through the word of the other characters. Other times, the reader must think carefully about a character’s words, actions, feelings, and thoughts to find out what the character is really like. Maniac Magee Literary Elements Chapters 6 - 9 Mood and Tone The mood of a story is the feeling that the story gives the reader. The Tone of a story is the author’s attitude toward the characters and events in the story. Main Idea and Details The main idea of a paragraph or chapter, tells what the whole section is about. Sometimes the main idea is directly stated. Other times, readers must figure out the main idea. Details tell more about the main idea. Author’s Inference Authors do not always explain every detail in a story. Readers must often figure out some things on their own. When you use information in a story and use your own experience to understand something that is not directly stated, you are making an inference. Maniac Magee Literary Elements Chapters 10 - 13 Dialogue Dialogue is what characters in a story say each other. You can learn a lot about characters from the words that they use with each other. Symbolism Symbolism is the practice of representing things by symbols, or of investing things with a symbolic meaning or character. A symbol is an object, action, or idea that represents something other than itself. Judgments Judgments are personal opinions supported by facts. Maniac Magee Literary Elements Chapters 14 - 17 Author’s Purpose Authors write for many reasons. The reason an author writes is called the author´s purpose. 3 of the mains reasons are: To inform readers by using descriptions, information, or directions. To entertain readers with enjoyable reading material. To persuade readers to believe or act in a certain way. . Multiple-Meaning Words Multiple Meaning Words are words that have several meanings depending upon how they are used in a sentence. We use context clues to help us figure out which meaning is correct. Prediction When you make a prediction, you guess what is going to happen in a story. In order to make a good prediction, you must think carefully about clues from the story as well as use your own knowledge and experience. Maniac Magee Literary Elements Chapters 18 - 21 Context Clues You can often figure out the meaning of a new word by thinking about the words and ideas around it. This is called using context clues. Flashback A flashback is literary device in which a story returns to an event that happened in the past. Authors use flashbacks to add interest to their story plots. Figurative Language Figurative language may compare two unlike things, give human qualities to things, or exaggerate meaning for effect. Maniac Magee Literary Elements Chapters 22 - 24 Compare and Contrast When you compare two things, you tell how they are alike. When you contrast two things, you tell how they are different. Foreshadowing Foreshadowing is a literary device in which clues from a story hint about events that might take place in the future. Authors use foreshadowing to add interest in their story plots. Generalization When you make a generalization, you draw a conclusion about all or most of the elements of a group. A valid generalization is one that is based on many consistent examples or facts. A faulty generalization is one for which there are many exceptions. Maniac Magee Literary Elements Chapters 25 - 28 Fact and Opinion A fact is a statement that can be proved to be true or untrue. An opinion is a statement that tells what a person thinks or believes. An opinion cannot be proved. Irony Irony occurs in a story when something happens that is the opposite of what is expected. Ironic situations often have humorous results. Point of View The person telling the story is called the narrator. The point of view of a story depends on who is narrating it. In the first-person point of view, the narrator is a character in the story who uses words such as I, me, and my. The character tells the story as if it were happening to him or her. In the third-person point of view, the narrator is someone outside of the story. The narrator uses words such as he, she, and they, and often knows the thoughts and feelings of all the characters in the story. Maniac Magee Literary Elements Chapters 29 - 32 Figurative Language Figurative language may compare two unlike things, give human qualities to things, or exaggerate meaning for effect. Writers use figurative language to help create vivid pictures in their reader´s minds. Context Clues You can often figure out the meaning of a new word by thinking about the words and ideas around it. This is called using context clues. Sound Devices Poets and authors use sound devices to add interest to their words. Four common sound devices are; Alliteration – two or more words with the same beginning sound. Rhyme – words or lines that end with the same sound. Repetition – using sounds or words over and over again. Onomatopoeia – words that imitate the sound they stand for. Prediction When you make a prediction, you guess what is going to happen in a story. In order to make a good prediction, you must think carefully about clues from the story as well as use your own knowledge and experience. Maniac Magee Literary Elements Chapters 33 - 35 Draw Conclusions When you draw a conclusion. You arrive at a decision based on clues in a story and your own knowledge and experience. Mood and Tone The mood of a story is the feeling that the story gives the reader. The tone of a story is the author´s attitude toward the characters and events in the story. Dialogue Dialogue is what characters in a story say to each other. You can learn a lot about characters from the dialogue they exchange with one another. Setting The setting of a story is the time and place in which the story takes place. The setting of a story often affects the way a character feels. Maniac Magee Literary Elements Chapters 36 - 38 Cause and Effect A cause is what makes something happen. The thing that happens is the effect. It´s important to look for cause-and-effect relationships as you read so that you can better understand a story and the characters in it. Compare and Contrast When you compare two things, you tell how they are alike. When you contrast two things, you tell how they are different. Judgments Judgments are personal opinions supported by facts. Maniac Magee Literary Elements Chapters 39 - 40 Figurative Language Figurative language may compare two unlike things, give human qualities to things, or exaggerate meaning for effect. Writers use figurative language to help create vivid pictures in their reader´s minds. Author’s Inference Authors do not always explain every detail in a story. Readers must often figure out some things on their own. When you use information in a story and use your own experience to understand something that is not directly stated, you are making an inference. Prediction When you make a prediction, you guess what is going to happen in a story. In order to make a good prediction, you must think carefully about clues from the story as well as use your own knowledge and experience. Judgments Judgments are personal opinions supported by facts. Maniac Magee Literary Elements Chapters 41 - 42 Draw Conclusions When you draw a conclusion. You arrive at a decision based on clues in a story and your own knowledge and experience. Word Referents Authors like to avoid repetitions to make their writing more interesting. To do this, they often use pronouns that stand for other words. These are called word referents. Point of View The person telling the story is called the narrator. The point of view of a story depends on who is narrating it. In the first-person point of view, the narrator is a character in the story who uses words such as I, me, and my. The character tells the story as if it were happening to him or her. In the third-person point of view, the narrator is someone outside of the story. The narrator uses words such as he, she, and they, and often knows the thoughts and feelings of all the characters in the story. Maniac Magee Literary Elements Chapters 43 - 46 Cause and Effect A cause is what makes something happen. The thing that happens is the effect. It’s important to look for cause-and-effect relationships as you read so that you can better understand a story and the characters in it. Context Clues You can often figure out the meaning of a new word by thinking about the words and ideas around it. This is called using context clues Judgment Judgments are personal opinions supported by facts. Theme The theme of a story is the most important message that the story gives a reader. Sometimes the theme is stated directly in a story. Other times, a reader must figure it out the theme by thinking about what happens to the characters and why it happens.