Trophic Levels Study Guide
advertisement

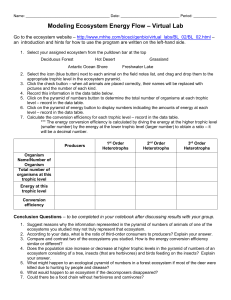
Trophic Levels Study Guide Relavent Sections of text Ch 54; pg 1233-1241 Objectives and study questions: 1. List the common trophic levels found within an ecosystem 2. What component (trophic level) within an ecosystem captures the energy of the sun and makes it available to other living things? 3. When energy passes from one trophic level to the next what happens to the amount of energy that is usable by the next trophic level. 4. What are the most common producers in a terrestrial ecosystem? 5. What are the most important producers in a aquatic/marine food chain? 6. What is the difference between a consumer and a producer? 7. Are primary consumers herbivores or carnivores? 8. Are secondary and tertiary consumers herbivores or carnivores? 9. At which trophic level(s) can detrivores/decomposers be found? 10. What is the difference between gross and net primary productivity 11. What are the two main limitations on primary productivity of aquatic ecosystems? Which is the most important? 12. What are the two main limitations on primary productivity of terrestrial ecosystems? Which is the most important? 13. What is a food chain and food web? 14. On average how much energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next level and is available for use? 15. What is the primary factor that limits the number of trophic levels in an ecosystem? 16. What does a energy pyramid describe about an ecosystem? 17. What does a biomass pyramid describe about an ecosystem? 18. Describe how bottom up controls on an ecosystem work. 19. Describe how top-down controls on an ecosystem work 20. What is bioaccumulation? 21. What is biomagnifications?