Algorithms - Ray Chambers
advertisement

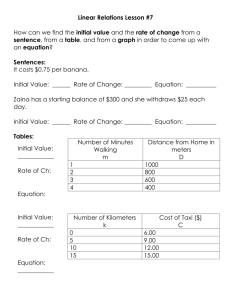
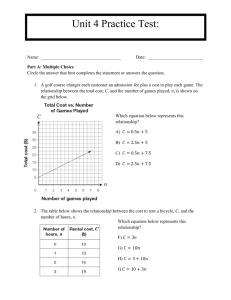
LO: We’re learning to understand how computers solve problems! Let's say that you have a friend arriving at the airport, and your friend needs to get from the airport to your house. Here is an algorithm that you might give your friend for getting to your home: The taxi algorithm: Go to the taxi stand. Get in a taxi. Give the driver my address. Let's say that you have a friend arriving at the airport, and your friend needs to get from the airport to your house. Here is an algorithm that you might give your friend for getting to your home: The taxi algorithm: Go to the taxi stand. Get in a taxi. Give the driver my address. In groups / individual, see if you can come up with other algorithms surrounding the scenario on the previous slide. Maybe it’s a bus from the terminal…. Sometimes it is easy to build an algorithm when you know how it works. Have a look at this flow chart below. Can you explain what is happening and why? Here is some guidance on the symbols. Splitting away from your group, pick one of your algorithms and see if you can build a flow chart which finishes. You are required to use a video tutorial to create an algorithm to check whether a student is old enough to buy a DVD or game. You will need to set up Table from a previous lesson before you can use an algorithm to test it. Video 8/9 shows students how to set up a table structure and how to search it. Once you have built this Algorithm, see if you can build your own. TIP – Use a FLOW CHART to plan it out before building it. Your teacher will support any coding. • An algorithm is a technical term for a recipe of instructions which are: • • • Unambiguous – Recipe can be interpreted in one way. Executable – Steps that the computer can actually carry out. Terminating – There needs to be an end to the program. • Use flow charts to help us plan out the order in which we test or make decisions in.