states of matter - School District 27J
advertisement

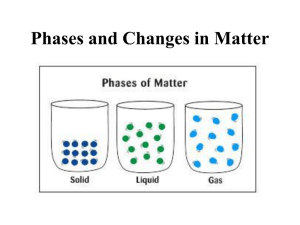
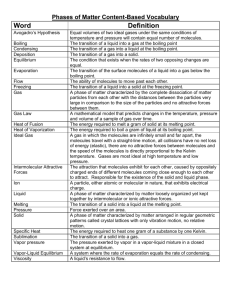
Context clues WARM UP: READ ARTICLE AND FIND ONE NEW VOCABULARY WORD. WRITE THE DEFINITION Vocabulary Write a sentence for: fish screen and discharge water What is a context clue? Vocabulary Write a sentence for: phase changes Boiling point Freezing point Temperature Step 1: go to sd27j.org Step 2: Pick Stuart Middle School Step 3: Staff- science- andrea lopez solorzano Step 4: 6th grade tab, chemistry unit, resources, gizmo Step 5: click enroll in a class: your username is student id and then password is studen1 Step 6: Enrollment code: Period 1:LCGCB2QMBW Period 4: RY5MGDEELW Period 5: E7TWGEUEJU Period 6: J8NPWKRRAC Vocabulary- now draw a picture Altitude – vertical distance, or elevation, above sea level. Boil – change from a liquid to a gas. Boiling point – the temperature at which boiling occurs. At sea level, the boiling point of water is 100 °C (212 °F). Water boils at lower temperatures at higher altitudes because air pressure is lower there. Freeze – change from a liquid to a solid. Freezing point – the temperature at which freezing occurs. At sea level, the freezing point of water is 0 °C (32 °F). Gas – a phase in which matter has no definite shape or volume. A gas will expand to fill any container. A gas can also be compressed. Molecules in a gas are relatively far apart and move freely. Water in the gas phase is called water vapor. Liquid – a phase in which matter has definite volume but no definite shape. A liquid will take the shape of a container but cannot expand or be compressed. Molecules in a liquid move randomly but stay close to one another. Vocabulary continued Melt – change from a solid to a liquid. Melting point – the temperature at which melting occurs. At sea level, the melting point of ice is 0 °C (32 °F). Phase – a state of matter with certain physical properties. Solid, liquid, and gas phases occur naturally on Earth. Plasma is a phase found in stars. Solid – a phase in which matter has a definite shape and a definite volume. A solid will retain the same shape and volume in any container. Atoms in a solid are held in a rigid structure and cannot move freely. Water in the solid phase is called ice. Discussion questions As students are working or just after they are done, discuss the following questions: What are some of the differences between solids, liquids, and gases? How does temperature relate to molecular motion? What causes materials to change phase? Why does the temperature stay constant during a phase change? Why do water pipes burst in the winter? Why does it take longer to cook pasta at high altitudes than at sea level? Complete worksheets A,B,C Follow step by step directions on worksheets. Then do the assesment Worksheet A Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) A family from Minnesota turns off the heat and flies to Florida for a winter holiday. When they come home, all of their water pipes have burst. What do you think happened? _________________________________________________________________________ Spaghetti takes about 9 minutes to cook at sea level, but about 14 minutes in the mountains. Why do you think this is so? _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Worksheet A continued In the Phase Changes Gizmo™, select the Micro view and set the Ice volume to 50 cc. Click Play ( ) and observe molecules in the solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (air) phases. In which phase(s) are the molecules held rigidly together? ______________________________________________ In which phase(s) do the molecules move freely? ______________________________________________ In which phase(s) are the molecules held in a defined shape? ________________________ In which phase(s) do the molecules take the shape of their container? _________________ Solid atoms or molecules held in a rigid structure. Atoms in the structure may vibrate, but do not move freely A solid has a definite shape and a definite volume Liquid molecules that are attracted to one another but can still move around so that they take the shape of their container. ‘ Liquids thus have a definite volume but an indefinite shape. gas rapidly moving molecules that move and collide freely. A gas will expand to occupy all the space in its container. Gases also can be compressed to a very small volume. Thus gases do not have a definite shape or volume Solid, liquid, gas When a solid is heated, the atoms begin to vibrate more and more rapidly. Eventually the vibrations are strong enough to break the rigid bonds holding the atoms together, and the solid melts into a liquid. During the melting process, temperature does not increase because the added heat energy goes into melting the solid rather than heating the liquid. In a liquid, the molecules move at a variety of speeds. The fastest-moving molecules can escape the surface of the liquid and become a gas. This process is called evaporation. As the liquid is heated, the average speed of the molecules increases until large bubbles of gas form within the liquid. This is boiling. The temperature remains constant during boiling because the fastest molecules are constantly leaving the liquid and escaping as gas. Cooling produces the opposite phase changes. As a gas is cooled, the molecules slow down until their mutual attraction causes them to clump together and form droplets of liquid. This is condensation. When a liquid is cooled, the molecules move slowly enough that they can begin to form rigid chemical bonds in a crystalline lattice. This is freezing