doc
advertisement
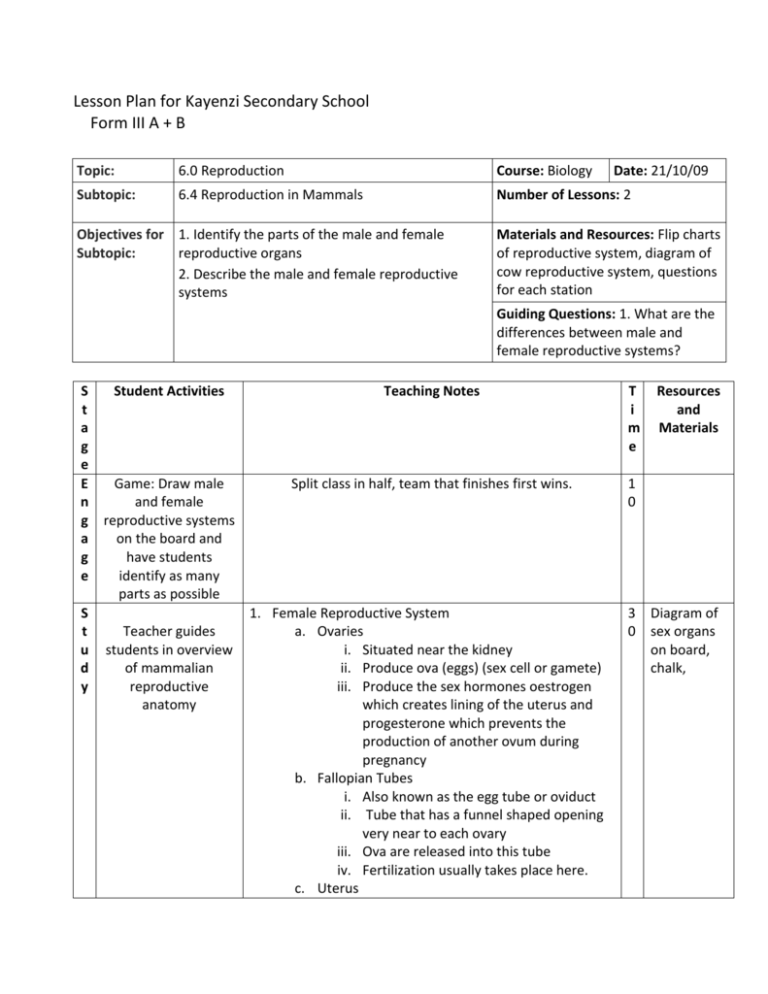
Lesson Plan for Kayenzi Secondary School Form III A + B Topic: 6.0 Reproduction Course: Biology Subtopic: 6.4 Reproduction in Mammals Number of Lessons: 2 Objectives for 1. Identify the parts of the male and female Subtopic: reproductive organs 2. Describe the male and female reproductive systems Date: 21/10/09 Materials and Resources: Flip charts of reproductive system, diagram of cow reproductive system, questions for each station Guiding Questions: 1. What are the differences between male and female reproductive systems? S Student Activities Teaching Notes t a g e E Game: Draw male Split class in half, team that finishes first wins. n and female g reproductive systems a on the board and g have students e identify as many parts as possible S 1. Female Reproductive System t Teacher guides a. Ovaries u students in overview i. Situated near the kidney d of mammalian ii. Produce ova (eggs) (sex cell or gamete) y reproductive iii. Produce the sex hormones oestrogen anatomy which creates lining of the uterus and progesterone which prevents the production of another ovum during pregnancy b. Fallopian Tubes i. Also known as the egg tube or oviduct ii. Tube that has a funnel shaped opening very near to each ovary iii. Ova are released into this tube iv. Fertilization usually takes place here. c. Uterus T i m e Resources and Materials 1 0 3 Diagram of 0 sex organs on board, chalk, i. The fallopian tubes unite and form an expanded tubular organ called the uterus or womb. ii. Thick walls made of muscle tissue iii. Zygotes or the fertilized ovum implant into the uterine wall and develop into an embryo iv. It is about the size of a fist but expands during pregnancy v. At the base is a small muscular ring called the cervix which leads to the vagina. d. Vagina i. This tubular opening connects the uterus to the outside of the body. ii. It is where sperm is deposited. 2. Male Reproductive System a. Testes i. Testes produce sperm (male sex cell or gamete) ii. also endocrine glands which secrete the sex hormone testosterone iii. A pouch of skin called the scrotum protects the testes. iv. The scrotum hangs away from the body and maintains the testes at a slightly lower body temperature (34 C) required in normal sperm development in humans. v. Epididiymis temporarily stores sperm. vi. From the epididimyis the sperm travels through the sperm duct or vas deferens which then transports sperm to the penis. b. Seminal vesicles and prostate gland i. The two seminal vesicles in conjunction with the prostate gland create a liquid which mixes with sperm as it passes through the vas deferens. The fluid provides nourishment and protection to sperm. ii. The combined sperm and liquid is called semen. c. Penis i. The penis is a copulatory organ. Copulation is the act of the male sex organ entering the female sex organ. ii. Used to introduce sperm into the vagina, called ejaculation. iii. The urethra carries both urine and semen. A c ti v a t e E v a l u a t e Break students into 4 groups. Have each complete the tasks written at each station in exercise book. Rotate every 10 minutes. 4 Male and 0 Female flip chart, definitions, where a sperm starts and ends Check over work at each station verbally and visually. Have students write questions about sex, STIs, pregnancy and collect.







