A&P Chapter 16 The Reproductive System
advertisement

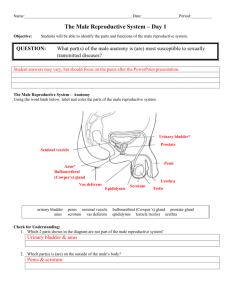
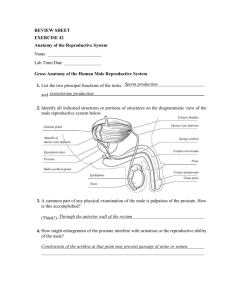
A&P Chapter 16 The Reproductive System 1. Summarize the function of the reproductive system. ---system ensures the continual existence of the human species ---is the only system NOT essential to the life of the individual ---human reproductive system produces, stores, nourishes, and transports functional male and female reproductive cells called gametes 2. Identify organs of the male reproductive system when provided with a model or diagram and discuss the general function of each organ. ---IDENTIFY AND LABEL THE FOLLOWING ON THE DIAGHRAM PROVIDED: penis (shaft, glans, and prepuce), testes, epididymis, ductus deferens, seminal vesicles, bulbourethral gland, prostate gland, urethra, and ejaculatory duct 3. Name the endocrine and exocrine products of the testes. ---endocrine products are the androgens of which testosterone is most important ---exocrine product is (are) sperm 4. Discuss the composition of semen and the glands that produce it. ---semen is a mixture of sperm and accessory gland secretions ---secretions supply the liquid that provides a transport medium and nutrients, and contains chemicals that protect the sperm and aid their movement ---semen is alkaline (pH 7.2-7.6) which helps neutralize the acid environment (pH 3.5-4) of the female’s vagina, protecting the delicate sperm and enhancing their motility ---semen also contains chemical that inhibits bacterial multiplication ---semen dilutes sperm to assist in their motility ---about 2-5 mls of semen in an ejaculation (50-130 million sperm/ml) ---seminal vesicles (located at base of bladder) produce about 60% of fluid volume of semen --thick, yellowish fluid rich in fructose, vitamin C, prostaglandins, and other substances which nourish and activate sperm passing through tract ---prostate gland is about the size and shape on an almond and encircles the upper prostatic part of urethra just below the bladder --secretes a milky fluid that plays a role in activating sperm --during ejaculation, it enters the urethra through several small ducts ---bulbourethral glands are tiny, pea-sized glands inferior to the prostate gland --they produce a thick, clear mucus that drains into the penile urethra --this secretion is first to pass down urethra when man becomes sexually excited --believed to cleanse the urethra of traces of acidic urine and serve as lubricant during sexual intercourse 5. Trace the pathway followed by sperm from the testis to the body exterior ---sperm produced in the testis seminiferous tubules and empty into another set of tubules called rete testis which are located at one side of testis ---sperm then travel through rete testis to enter first part of the duct system called the epididymis which hugs the external surface of the testis --sperm take about 20 days to make their way through epididymis --while there, they complete their maturation process and gain ability to swim --when male is sexually stimulated, walls of epididymis contract to expel sperm into next part of the duct system called the ductus deferens (vas deferens)