Financial Ratio Analysis
advertisement

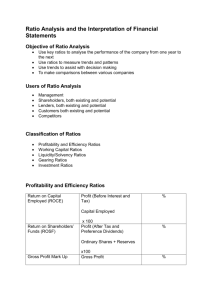
July 8, 2011 Financial Ratio Analysis Financial ratios combine different financial parameters. They are based on the financial data drawn from the balance sheet and the P&L account. Each ratio is studied both by itself and along with other ratios, in order to gain critical insights. Different ratios are used to analyse the different dimensions of a business. TCS Financial Ratios ( 2009-10) 3 TCS Financial Ratios ( 2009-10) 4 Wipro Financial Ratios ( 2009-10) 5 Profitability ratios These ratios measure how profitable the business is with respect to sales and assets. 6 Gross Profit Margin = (Sales – Cost of Goods Sold) ÷ (Sales) Operating profit margin (Gross Profit – SG&A - R&D ) ÷ (Sales) 8 Net Profit Margin = (Profit After Tax) ÷ (Sales) Return on Assets = (Profit After Tax) ÷ (Total Assets) Return on Investment (ROI) The return on investment is computed as under: ROI = [(PBIT) ÷ (Total Capital Employed)] = [(PBIT) ÷ (Shareholders’ Net Worth + Borrowings)] Activity ratios These ratios measure how efficiently the assets of the business are being used. 12 Inventory Turnover Ratio = (Cost of Goods Sold) ÷ (Inventory) Average Collection Period (Debtors Turnover) = (Debtors) ÷ (Average Daily Sales) Capital Employed Turnover = (Sales) ÷ (Capital Employed) Fixed Assets Turnover = (Sales) ÷ (Net Fixed Assets) Liquidity Ratios These ratios measure to what extent the business has funds available to meet its obligations. 17 Current Ratio = (Current Assets) ÷ (Current Liabilities) Quick Ratio or Acid Test Ratio = (Quick Assets) ÷ (Current Liabilities) Quick assets = Current assets - Inventory Leverage ratios These ratios measure the extent of financial risk assumed by the business, ie the level of debt in relation to equity. 20 Debt-Equity Ratio = (Long Term Debt) ÷ (Shareholders’ Net Worth) Total Debt to Total Capital Employed Ratio = (Total Debt) ÷ (Total Capital Employed) Coverage ratios These ratios measure the availability of funds to meet various financial obligations. 23 Interest Coverage = (Profit Before Interest and Tax) ÷ (Interest Charges) Dividend Cover = (Profit after Tax less Preference Dividend) (Equity Dividend) ÷ Debt Service Coverage Ratio = (Profit Before Interest and Tax) ÷ (Loan Installments + Interest) Shareholder Returns These ratios measure how well the shareholders are being rewarded by the company. 27 Return on Shareholders’ Net Worth = (Net Profit After Tax – Pref. Dividend) ÷ (Equity Shareholders’ Net Worth) Earnings Per Share (EPS) = (Net Profit After Tax – Pref. Dividend) ÷ (Number of Equity Shares) Dividend Per Share = (Dividends paid to Equity Shareholders) ÷ (Number of Equity Shares) Dividend Pay-out Ratio = (Dividend per share) ÷ (Earnings per Share) Dividend Yield = (Dividend per share) ÷ (Market Value per share) Earnings Yield = (Earnings per share) ÷ (Market Value per share) Valuation ratios These ratios are useful in arriving at a realistic valuation of the business. 34 Price/Earnings Ratio (P/E ratio) = (Market Value per Share) ÷ (Earnings per share) Book Value per Share = (Net Worth – Preference Share Capital) ÷ (No of shares) Market Price to Book Value = (Market Price per Share)÷ (Book Value per share) Thank You 38