Part 1
advertisement

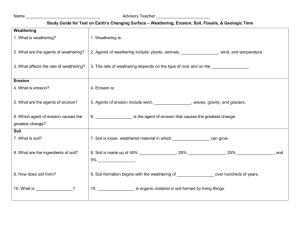
WEATHERING AND EROSION UNIT 4 STUDY GUIDE Unit Test on ______________. - Changing Earth’s Surface THE BIG IDEA OF THIS UNIT: Weathering, erosion, and deposition act together in a cycle that wears down and builds up the Earth’s surface. Weathering the process by which rock is broken down very slowly (much slower than earthquake activity, landslides, or volcanic activity) Just breaking downnot moving yet! Mechanical Weathering breakdown of rock into smaller pieces by physical means The rock is still a rock, just smaller. Ice Wedging alternate freezing and thawing of water that seeps into the cracks of rocks and cause breakage Ex. potholes Ice Wedging Yosemite National Park, California Abrasion the grinding and wearing away of rock by wind, water, or gravity Exfoliation the peeling or flaking of rock due to repeating heating and cooling Exfoliation Plants the roots of plants grow down into the rock and eventually bust it apart (root pry is an example) Root Pry Animals can wear down rock as well Animals Animal burrowing causes weathering to occur. Chemical Weathering rock breaks down as a result of a chemical reaction It doesn’t just look different, it IS different! Acid Precipitation rain, sleet, or snow that contains a high concentration of acids (sulfur, nitrogen, and carbon oxides); acid rain can dissolve the limestone that is on some buildings. Acid Precipitation Plant acids (Humic acids) moss and lichens, which are fungi and algae living together, can break down rock Oxidation oxygen in the air can cause rust Weathering creates sediments. Then, sediments get carried away. Erosion- the process in which weathered rock and soil (sediments) are transported/ moved from one place to another; Example – The Rocky Mountains have sharp peaks and are younger than the Appalachian Mountains because they haven’t been eroded as much. Erosion 4 Agents (causes) of Erosion: 1) 2) 3) 4) Gravity Water Wind Waves 1) Gravity/Mass Movement when gravity pulls rocks and soil downhill a. Landslide – sudden mass erosion of rocks, trees, and soil downhill Landslide Video • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CUXhjP kGBtU Gravity/Mass movement b. Mudslide- sudden mass erosion of mud downhill Click on the video link. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n1cCs-S5EKc Gravity/Mass Movement c. Creep – slow movement of soil, rocks, and plants down a slope where plant roots and tree trunks begin to lean toward the soil as erosion continues Creep - The Force of Moving Water 2) Water happens when water picks up materials and carries them away; running water changes the Earth’s surface more than any other agent a. Runoff – water flowing across the Earth’s surface; most sediment washes or falls into a river b. Rivers – V-shaped valleys and canyons can be caused by erosion from running water c. Glaciers – frozen “rivers of ice” that can make Ushaped valleys - Glaciers How Glacier Erosion Shapes the Land V-shaped by water, followed by U-shaped by ice U-shaped Valley 3) Wind occurs when wind picks up loose sediments and carries them in the air - Wind Wind Erosion SANDSTORM LEAVING NORTH AFRICA TOWARDS THE ATLANTIC – CANARY ISLAND. Wind Erosion- The Dust Bowl Wind erosion is one cause of soil loss. For example, wind erosion contributed to the Dust Bowl on the Great Plains. The Dust Bowl ruined farmland in western Oklahoma and parts of the surrounding states. Wind blew dry particles of soil into great clouds of dust that traveled thousands of kilometers. Slide 6