IB Language and Literature: Introduction to the course
advertisement

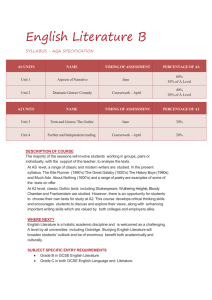
Part 1 - Language in Cultural Context – Aug-Nov 2013 Texts are chosen from a variety of sources, genres and media. Written Task x2 Further Oral Activities (15%) - Students complete at least two further oral activities, one based on part 1 and one based on part 2 of the course. Part 4 - Literature – Critical study (IOC – 15%) Nov-May 2014 Students comment on an extract from a literary text studied in part 4 of the course. (30 marks). Students are given two guiding questions. Texts: 1) Selected Poems – Wilfred Owen (Poetry, Europe, 20thC) 2) Othello – William Shakespeare (Drama, Europe, 16/17thC) 10 minute commentary 5 minute discussion and questions Part 2 - Language and Mass Communication – May-Oct 2014 Texts are chosen from a variety of sources, genres and media. Written Task Further Oral Activities (15%) - Students complete at least two further oral activities, one based on part 1 and one based on part 2 of the course. Part 3 – Exam (Paper 2 – 1hr 30 mins) – Oct-Apr 2015 Texts and Contexts (25%) In response to one of six questions students write an essay based on both the literary texts studied in part 3. The questions are the same at HL but the assessment criteria are different. Texts: A Doll’s House by Henrik Ibsen (Drama, Europe 19th C) A Streetcar Named Desire by Tennessee Williams (Drama, US, 20th C) Paper 1 – Exam (1hr 30 mins) Textual Analysis (25%) The paper consists of two unseen texts. Guiding Questions provided The exam builds on the skills learned in Parts 1 and 2 Areas to be covered in this part include: Language and the individual Language and communities Language and power Language and knowledge Language and gender Written Task #1 completed Further Oral Activity completed Preparation for Paper 1 practice paper Annotating sample papers There are 3 main objectives for this term you should become familiar with… the use of persuasive language in political speeches the features of SMS messages postcolonial re-readings of texts. the impact of electronic communication on meaning the influence of government policy the emergence of new vocabulary from the language of groups (for example, young people) the disappearance of vocabulary and of languages themselves. the ways in which jargon and professional language are used the ways in which language affirms identity the status given to standard and nonstandard forms of the language the status of minority languages in multilingual societies.