PPTX - PMI Baltimore Chapter
advertisement

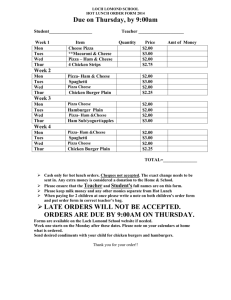
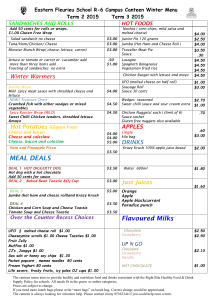
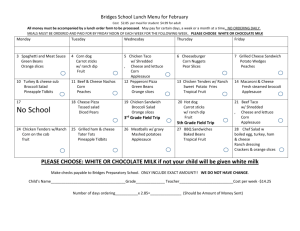
CHANGE MANAGEMENT The Project Manager as an Agent of Change Mary T. Dirlam, PMP Thursday, July 19, 2012 WHAT DO ALL PROJECTS HAVE IN COMMON? Projects introduce change PMs deliver projects PMs are therefore Agents of Change WHAT IS CHANGE? Standard definition: A transformation, modification or alteration Our Reality: Making people do something different than how they are used to doing it WHAT IS CHANGE MANAGEMENT Countering the natural organizational resistance to change Pioneers: Elisabeth Kubler-Ross: worked with terminally ill patients Spencer Johnson: writer of business fables John P. Kotter: Harvard Business School professor and organizational change expert KUBLER-ROSS: PHASES OF GRIEF Denial – “This isn’t happening” • Anger – “Why is this happening?” • Bargaining – “I’ll do anything to delay/stop this from happening” • Depression – “Why bother if this is happening anyway” • Acceptance – “This is going to happen, and everything will be OK” • SPENCER: “WHO MOVED MY CHEESE” • • • • • • • Change Happens – They keep moving the cheese Anticipate Change – Get ready for the cheese to move Monitor Change – Smell the cheese so often you now when it is getting stale Adapt to Change Quickly – The quicker you let go of the old stale cheese the sooner you can enjoy the new fresh cheese Change – Move with the cheese Enjoy Change – Savor the adventure and enjoy the taste of the new cheese Be Ready to Change Quickly and Enjoy It Again – They keep moving the cheese KOTTER: “LEADING CHANGE” • • • • • • • • Create a sense of urgency – Why this is important Develop a guiding coalition – How will this be implemented Develop a vision for the future – What will things look like after this is implemented Communicate the vision – What you need to know about what we are implementing Empower broad-based action – How you can have an impact Generate short-term wins – What can we achieve now Don’t let up – How to stay committed Make it stick in the organizational culture – How this is part of the organization’s long-term plan for success HOW DOES CHANGE MANAGEMENT FIT INTO PROJECT MANAGEMENT? How do we define project success? How are long-term usability and customer satisfaction factored in? Who owns change management – PM or stakeholders? Or is it a partnership? CHANGE MANAGEMENT AS PARTNERSHIP Engage Operations Management early Leverage Subject Matter Experts from the business Provide regular communications to business stakeholders and impacted business units The role of Business Process Design Shared ownership of training Communications planning with an eye on change Change Management as part of Project Management PROJECT KNOWLEDGE AREAS Integration Management • Scope Management • Time Management • Cost Management • Quality Management • Human Resource Management • Communications Management • Risk Management • Procurement Management • DEFINING A CHANGE MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE AREA Change Planning – create a change management plan for how changes to current processes will be documented and communicated to project stakeholders • Change Definition – identify and document processes and procedures that will be impacted by the implementation of project deliverables • Control Change – execute change management as defined in the change management plan • Change Verification – document the impact of the project deliverables and the effectiveness of the change management plan for lessons learned • 1. CHANGE PLANNING Inputs Enterprise Environmental Factors Organizational Process Assets Project Communications Plan Project Timeline Tools and Techniques Expert Judgment Templates, forms and standards Outputs Change Management Plan 2. CHANGE DEFINITION Inputs Organizational Process Assets Project Scope Statement Approved Change Requests Tools and Techniques Product Analysis Process Analysis Expert Judgment Outputs Process Documentation – Current State Process Documentation – Future State 3. CONTROL CHANGE Inputs Change Management Plan Completed Deliverables Process Documentation Tools and Techniques Organizational Process Assets Expert Judgment Templates, forms and standards Outputs Approved Communications 4. CHANGE VERIFICATION Inputs Approved Communications Stakeholder Feedback Tools and Techniques Process Analysis Outputs Change Management Plan Updates Communications Management Plan Updates Organizational Process Assets Updates ADDITIONAL READING On Death and Dying – Elisabeth Kubler-Ross Who Moved My Cheese? – Spencer Johnson Leading Change – John P. Kotter A Pocket Full of Change – Peter de Jager