Revision - FHS Geography
advertisement

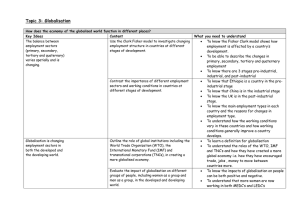
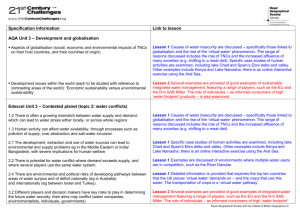
Globalisation Topic 3 What does globalisation mean? Definition Globalisation is the process by which the world is becoming increasingly interconnected as a result of massively increased trade and cultural exchange. Why has globalisation occurred? Make a list of 5-10 factors that have lead to globalisation. Eg. a) Increased access to technology eg the internet Check your answers against this: Better methods Of communication e.g. internet, phone Low transport costs Different job opportunities in countries Its easier to trade between Countries now Lower wages in LEDC countries One of the reasons is EMPLOYMENT STRUCTURES Definition Primary Characteristics Quaternary EG 2 Extracting raw materials Secondary Tertiary EG 1 baker Office job teacher App/website designer Primary industry/sector Secondary industry/sector Tertiary industry/sector Quaternary sector/industry Employment sectors Primary – people extract raw materials from the l____ or s__ e.g. f______, mining, f_____ Secondary – involves m_________ where raw materials are converted to a finished product e.g. textile and car p_________ Tertiary – provide a s______e.g. distribution, retailing, financial services, nursing, t_______ Quaternary – provide information and expert help e.g. Creative/knowledge based industries, ____ based The Clark Fisher Model What does this model show? How does it relate to the UK? How has this lead to globalisation? Explain how employment structures change over time in countries. Clark and Fisher believed that countries employment structures changed in three stages due to the development of their economies. In stage one (Pre-industrial times) countries had high\low percentage of people in primary/secondary/tertiary industry and a low percentage in in primary/secondary/tertiary industry. This meant countries were poor because …….. In stage two (Industrial times); countries employment structure starts to change. Describe the changes. This means countries are beginning to earn more money because…… In stage three …………….. Global trade FDI Foreign Direct Investment WTO World trade organisation How have these key ideas helped to develop globalisation? P190-195 Lower transport costs TNC’s Transnational cooperation's IMF International monetary fund TNCs Define TNCs Egs Characteristics Define: a) growth b) merger c) consolidation d) conglomeration How does FDI link to TNCs? All of these factors has allowed TNC’s to globalise the world What are TNC’s? Can you think of anymore? You are going to create a case study on Nike Why have Nike ‘outsourced’ to other countries? What does outsourcing mean? Page 200-201 Advantages For TNCs For host countries Disadvantages Case Study: BT Why has BT outsourced to Bangalore? (5 reasons) What is meant by the ‘new economy’ and ‘footloose industries’? (p199) Using examples, explain how outsourcing can affect different countries different ways (6) WTO – The World Trade Organisation What are trade barriers? How can they affect globalisation? Who benefits the most/least from trade barriers? Exam question Using examples, explain how organisations like the IMF and WTO can help the process of globalisation. (6) Exam question Explain how Globalisation has led to greater trade between countries (4) Using examples, explain how TNC’s operate in different parts of the world (6) How does employment differ in Malawi, Vietnam and the UK? Brainstorm with 3 different diagrams Copy and complete Malawi Stage in the Clark Fisher Model Main employment Characteristics of job Advantages of main employment sector Disadvantages of main employment sectors Vietnam UK Exam questions: • Using examples, explain why employment in developing countries has changed in recent years (6) • Identify four pieces of evidence to show that Vietnam is a more industrialised country than Malawi (4) • Outline one benefit and one problem that industrialisation can bring to a country (4) Case Study: Leeds Outline: 1. How globalisation has affected Leeds 2. The impacts (+ve/-ve) on groups of people (4 different groups needed) Case Study: Bangladesh Outline: 1. How globalisation has affected Bangladesh 2. The impacts (+ve/-ve) on groups of people (4 different groups needed) Exam question Using examples, describe how globalisation can impact on men and women in developed countries (6) Using examples, explain why globalisation can lead to unequal impacts on men and women in developing countries (6) Exam question Using examples, explain how outsourcing can affect different countries in different ways (6)