Human Topic 3 Globalisation
advertisement
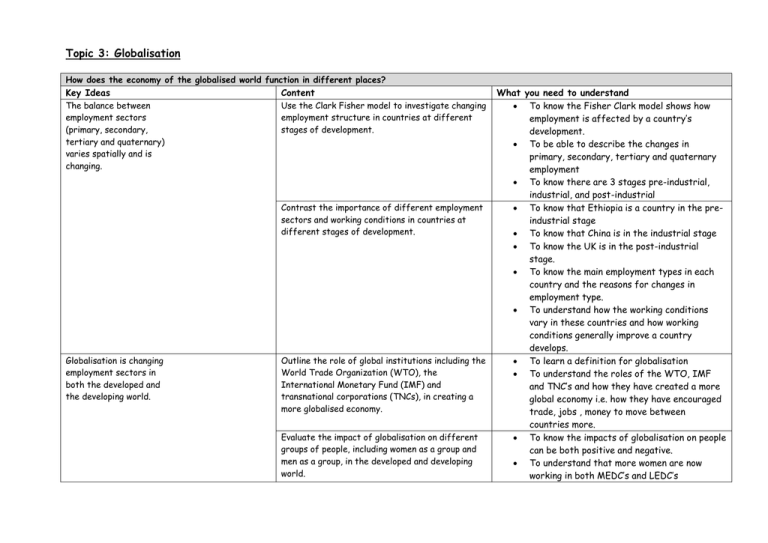
Topic 3: Globalisation How does the economy of the globalised world function in different places? Key Ideas The balance between employment sectors (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary) varies spatially and is changing. Content Use the Clark Fisher model to investigate changing employment structure in countries at different stages of development. Contrast the importance of different employment sectors and working conditions in countries at different stages of development. Globalisation is changing employment sectors in both the developed and the developing world. Outline the role of global institutions including the World Trade Organization (WTO), the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and transnational corporations (TNCs), in creating a more globalised economy. Evaluate the impact of globalisation on different groups of people, including women as a group and men as a group, in the developed and developing world. What you need to understand To know the Fisher Clark model shows how employment is affected by a country’s development. To be able to describe the changes in primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary employment To know there are 3 stages pre-industrial, industrial, and post-industrial To know that Ethiopia is a country in the preindustrial stage To know that China is in the industrial stage To know the UK is in the post-industrial stage. To know the main employment types in each country and the reasons for changes in employment type. To understand how the working conditions vary in these countries and how working conditions generally improve a country develops. To learn a definition for globalisation To understand the roles of the WTO, IMF and TNC’s and how they have created a more global economy i.e. how they have encouraged trade, jobs , money to move between countries more. To know the impacts of globalisation on people can be both positive and negative. To understand that more women are now working in both MEDC’s and LEDC’s What changes have taken place in the flow of goods and capital? In the past 50 years both Examine the changes in the volume and pattern of international trade and international trade and foreign direct investment. the flow of capital across international borders have expanded rapidly. Explore the reasons for these changes, including lower transport costs, TNC growth and mergers and state-led investment. Transnational corporations (TNCs) control a substantial part of the global economy and have created a global shift. Study one TNC in the secondary sector to show how it operates in different parts of the world, e.g. location of headquarters, outsourcing and the global shift in manufacturing. Study one TNC in the tertiary sector to show how it operates in different parts of the world, e.g. administrative work moving overseas, globalisation of products, including the growth of retailing chains. To understand that the amount of trade has increased. To be able to interpret a map or diagram about the pattern of this trade – imports/exports To understand the Foreign direct investment is when a business from one country invests money in a company in another country or builds its own factory in another country To know that reduced transport cost have increased trade To understand how TNC’s have increased trade and the movement of goods. To know what mergers are (Pixar) To understand why some governments would invest in other countries e.g. China-Nigeria To learn Nike case study and know why it operates in different countries To learn Tesco case study and know why it operates in different countries.