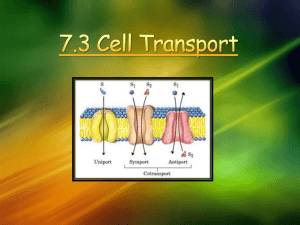
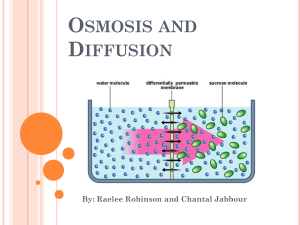
7.3 Cell Boundaries
advertisement

Explain the significance of the selectively permeable membrane to the transport of molecules. Predict the movement of molecules across a selectively permeable membrane (diffusion, osmosis, active transport) needed for a cell to maintain homeostasis given concentration gradients and different size molecules. Explain how water is important to cells (body temp., soluble environment, reactant in chemical reaction, maintains turgidity). Identify that water is important to cells. Explain how water is important to cells. Predict movement of molecules across a selectively permeable membrane needed to maintain homeostasis. Compare and contrast process used in movement of molecules across a semipermeable membrane, taking energy use into consideration. Cell Membrane – flexible barrier of cell that regulates what enters and leaves the cell. The cell membrane is “semipermeable”. Cell Membrane – flexible barrier of cell that regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Cell Wall – protects cell and give cell structure. • Found only in plant cells. What does permeable mean? What does semi permeable mean? In a solution, particles move constantly. Diffusion – tendency of particles to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. When do the particles of solute stop moving? When the concentration of solute is the same throughout, and the system has reached equilibrium (homeostasis). Water diffuses across membranes more easily than other substances. Osmosis – diffusion of water across semipermeable membrane. Which of the following is an example of diffusion? a. A student sprays perfume and it moves throughout the room. b. Food coloring is added to a beaker of water and slowly spreads during a science experiment. c. Both a and b are examples of diffusion. d. None of the above are examples of diffusion. SMART Response Qu To set the properties right click and select SMART Response Question Object->Properties... During diffusion, particles move from… a. Area of high concentration to area of low concentration. b. Area of low concentration to area of high concentration. c. They don’t move…they’re just particles. d. Areas where they will explode SMART Response Qu To set the properties right click and select SMART Response Question Object->Properties... How much energy does a cell use for diffusion? Cell uses ________ energy for materials to get into cell for DIFFUSION or OSMOSIS. We have more to go for this section. We will begin a lab later in the week. Vocabulary for homework. Explain the significance of the selectively permeable membrane to the transport of molecules. Predict the movement of molecules across a selectively permeable membrane (diffusion, osmosis, active transport) needed for a cell to maintain homeostasis given concentration gradients and different size molecules. Explain how water is important to cells (body temp., soluble environment, reactant in chemical reaction, maintains turgidity). Identify that water is important to cells. Explain how water is important to cells. Predict movement of molecules across a selectively permeable membrane needed to maintain homeostasis. Compare and contrast process used in movement of molecules across a semipermeable membrane, taking energy use into consideration. What is diffusion? Why does diffusion occur? What is osmosis? Find out who is the oldest…hypertonic Find out who is in the middle…hypotonic Find out who is the youngest…isotonic Three types of solutions: 1) Hypertonic – “above strength” Three types of solutions: 1) Hypertonic – “above strength” 2) Hypotonic – “below strength” 3) Isotonic – “same strength” For organisms to survive their cells must balance the intake of water, salts, sugars, and other molecules. 1) 2) 3) 4) What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis? Which type of solution is considered “same strength”. Which type of solution is considered “above strength”. Which type of solution is considered “below strength”. Don’t forget about the vocabulary worksheet from Monday. Chap. 7 Review • Pg. 189 1-6 OMIT #5 • Pg. 197 20-23 Wednesday/Thursday we’ll do a case study, finish notes (just a little left), and talk about hand washing lab, build cell transport foldable. Describe the importance of selectively permeable membrane to the transport of molecules. Predict the movement of molecules across a selectively permeable membrane needed for a cell to maintain homeostasis. Explain how water is important to cells. 1) 2) 3) 4) What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis? Which type of solution is considered “same strength”. Which type of solution is considered “above strength”. Which type of solution is considered “below strength”. What if a cell is placed into a hypertonic solution? What if a cell is placed into a hypotonic solution? What if a cell is placed into a isotonic solution? So why don’t our cells burst open shrivel up? Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Some molecules seem to pass through the cell membrane more easily than they should. Example: RBC’s have a glucose (sugar) channel that allows glucose to pass in and out. • Only glucose can pass through the channel. Facilitated Diffusion – is the diffusion of particles through protein channels. Hundreds of channels have been found to allow only one specific material through. • Carbohydrates and sugars mostly Hyper link Active transport – transport of materials that requires energy. • Uses “pumps” that are found in the membrane. The most common pump is the sodium (Na) – potassium (K) (salts) pump. Uses energy to move molecules from low to high concentration (against concentration gradient). Hyper link PASSIVE TRANSPORT 1) 2) 3) Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion NO ENERGY REQUIRED!!! ACTIVE TRANSPORT 1) Active Transport REQUIRES ENERGY!!! Review questions: What do we call the diffusion of water? How do large molecules diffuse into a cell when they are too large to pass through the cell membrane? What is the difference between active transport and passive transport? What are three examples of passive transport? Have a good weekend!