Learning Theories
advertisement

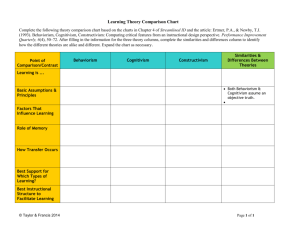
Olivia De Leon EDTC 3320 Professor Matthew Crosslin Behaviorism and cognitive are two psychological perspectives that have had an impact and dominated adult education/training program. These two different perspectives are major approaches to how people learn. Behaviorism is defined as a change in behavior from a result of an experience. Is a behavior that can be measured and observed. Behaviorism is observable changes in behavior. Learning is the result of changes in behavior. Human learning and behavior is controlled by experience. Behavioral theorists believe that human behavior is learned through observation. Theorists agree that behavior is represented by learned habits. A theorist that agree with this approach is Ivan. P. Pavlov who is a Russian scientist. Pavlov develop a classical conditioning analysis model to describe this type of learning. Pavlov developed the classical conditioning model. Classical conditioning is the emotional and psychological responses to stimuli. Behavior is controlled by association. He experimented this approach with dogs. The results were as follow: Stimulus Response Before conditioning, bell None Bell + meat placed in front initiated salivation The bell alone produced no response but when salivation initiated produce response to bell. Behaviorism Theory Today Who uses this theory now a days? Most adults need this method to successfully master a lesson. For example driving for someone who already knows how to drive is simple but imagine an adult trying to learn how to drive. Many people have to go thru virtualized driving schools to effectively learn how to drive. They have to see so they can follow. Even when using new technology most teenagers and adults go to popular web sites like youtube.com to see how things work so they can reproduce the action. As you can see this method of “show and follow” is essential for many citizens to succeed. Cognitivism is learning through repetition. Cognitivism evolved replacing behaviorism perspective. Cognitivists agree that learning is through active participation. “The mind works in the same way as a computer.” Information comes in, then is processed, leads to results. Cognitivists agree that for something to learned, there must be an opportunity to practice and then develop solutions. To be able to learn attitudes, first the learner must be exposed to models or arguments. R. Gagne agree and was a contributor to this approach. He was well-known for his stimulus-response theory. Gagne believe that cognitivism meaning is the ability to control the individual’s behavior to learn, remember and think. He believed that internal and external conditions are important to break down humans’ learned capabilities. Internal= information learned prior to instruction External=instruction provided to the learner. It deals with stimuli that is presented externally to the learner. The act of repeating the main idea to learn the main point of a instructional segment is still used today. Many instructors and teachers in school districts use this method especially when dealing with adults. For example, at United Independent School District in Laredo Tx. We have a time management device called the Kronos in order for the adult staff to successfully punch every morning they had to be trained repeatedly. Some of them understood the method rather quickly but most of them need the Cognitive Method to be successful. Bustamante, L., Howe-Tennant, D., & Ramo, C. (n.d.). Behaviorism Approach . SUNY Cortland - Faculty and Staff Web Services. Retrieved June 24, 2011 fromhttp://facultyweb.cortland.edu/andersmd/BEH/BEHAVIOR.HTML Corry, M. (n.d.). Gagne's Theory of Instruction. home.gwu.edu. Retrieved June 25, 2011 from http://home.gwu.edu/~mcorry/corry1.htm Mergel, B. (n.d.). Learning Theories of Instructional Design. University of Saskatchewan. Retrieved June 25, 2011 from http://www.usask.ca/education/coursework/802papers/mergel/brenda.htm Outline of Educational Learning Theories and Theorists. (n.d.). Educational Learning Theories and Theorists. Retrieved June 25, 2011 from http://www.teachersgarden.com/professionalresources/learningtheorists.html