midterm - LTMS525 How Do Humans Learn
advertisement

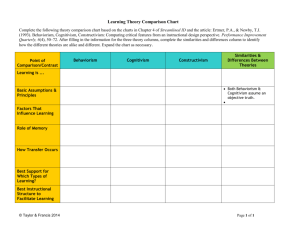
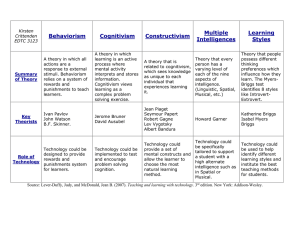
Mid-Term LTMS525 How Humans Learn There are six questions below. Complete 5 of the six questions. Make sure your answers are thorough and well written. 1. Discuss in written format the ways that Behaviorism influenced Social Cognitivism. Present an example of how Social Cognitivism is used in teaching. By blending the behaviorist theories of reinforcement and punishment with cognitive theories of awareness and exceptions, each set of variables can influence the other in reciprocal ways. Social cognitivism has been known as a bridge between behaviorist and cognitive learning because it encompasses attention, memory, and motivation. Social cognitivism states that the world and a person’s behavior cause each other, while behaviorism essentially states that one’s environment causes one’s behavior. By presenting that people are influenced by their environment, behaviorists helped social cognitive theorists to propose that over time people will regulate their own behavior. People will develop their own standards for performance, observe and evaluate themselves, and then reinforce and punish themselves accordingly. As teachers, modeling is a common technique used in instruction. When objectives involve teaching new skills, modeling provides an effective and more efficient style of instruction. Modeling is not restricted to planned instruction, but teachers must be careful that their behaviors reflect fairness acceptance of diverse viewpoints, a healthy lifestyle and high ethical standards. 2. What role has behaviorism and Cognitivism played in shaping the online learning environment? Cognitivism has centered around the theory of connectivism, which asserts that knowledge is distributive. It is not located in any given place (and therefore not 'transferred') but rather consists of the network of connections formed from experience and interactions with a knowing community. It is also an approach to learning that is based on conversation and interaction, on sharing, creation and participation, on learning not as a separate activity, but rather, as embedded in meaningful activities. Many on-line games or workflows offer the conversations and interactions necessary for connection. Behaviorism focuses on observable and measureable behaviors. Many of the online programs have a way for students and teachers to measure progress through varied reports. Online tools also provide the opportunity for remediation based on the students’ response. Online tools have come a long way in providing connections for learners to be successful. 3. Describe how the components of memory development can be used to improve learning. (include references to storage, knowledge, retrieval). Teachers should aid students in all parts of memory development through storage, knowledge, and retrieval. During storage, teacher should highlight the important information, explicitly tell what information is important, require students to rehearse, and elaborate on the material, as well as, provide visual aids to enable students to store the information appropriately. Teachers need to self check for meaningful learning, which is when students understand the information being presented. While assisting memory development through knowledge, teacher should provide students with strategies to encode knowledge through symbols, imagery, and small units to make connections between ideas. The four forms of knowledge (declarative versus procedural, and explicit versus implicit) give the basis for the importance of knowledge. Instruction with declarative knowledge helps students to remember people or places in their lives pertaining to information. In contrast, procedural knowledge involves completing a procedure, sometimes compared to “rote memory”. Procedural knowledge is the “how to do things”. As far as assisting memory through retrieval, teachers should make sure to present information to students in an organized manner so that students can recall it in that way. Information that must be retrieved within a particular context should be stored within that context. Information relevant to a situation is more likely to be retrieved when stored with other information about that situation. Being able to retrieve prior knowledge is essential to the learning process. 4. Explain how learner-directed instruction could be used for teaching a topic covered in our course. Instruction where the learner has considerable say in the issues they address and how they address them would be an example of learner-directed instruction. In our course, the latest chapter review would be an example of learner directed instruction. Groups were given the choice of what presentation tool to administer in presenting their understanding of the chapter. As we, the learners, control how to move around the content we are able to manage at our own pace. Our own initiation will guide our direction for learning. Our group viewed the given website that listed 50+ Web 2.0 tools and self-selected what we thought would work best for presentation of our material. We came to an agreement that Prezi would be the common tool and are now free to work independently as learners. We have our own sections of the chapter to include and must now take the initiative to direct our focus on those areas. As we come together on-line this week, we will compile one presentation of multiple learners that were directed by their own learning styles. Our final presentation will then be available to the group. 5. Define the Dual-Store Model of Memory. Then discuss some of the challenges theorists have made to this model of memory. The dual storage model is made up of 3 components. The first component, sensory register, holds virtually all incoming information for a very short amount of time. If this information is not processed in some fashion it may disappear from the memory system. Information that is processed would then move on to working memory, also called short-term memory, which is the second component. Working memory has a limited capacity and information stored here only lasts about 5 to 20 seconds unless it is processed further. The third component, long-term memory, is where information goes if it undergoes additional processing. Long-term memory appears to have the capacity to a great deal of information for a relatively long time. The two types of memory are what make up the model. Some evidence suggests that conscious processing in some sort of “working memory” is not always necessary for learning to occur. There are alternative views of memory that present depth of processing as an important factor affecting learning. They suggest that memory is only one large entity of which only a tiny portion can be activated at a time. No matter what the focus though, the dual-store model continues to be a popular mechanism for helping to understand the nature of human memory.