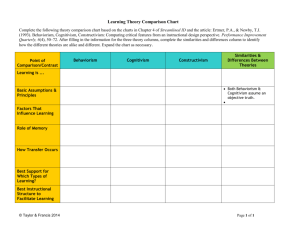
Learning Theories: Behaviorism, Cognitivism, Constructivism
advertisement
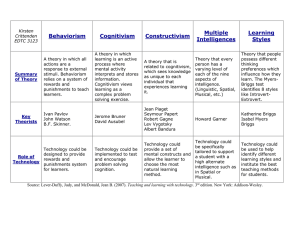
Cheryl Denny • Behaviorism • Cognitivism • Constructivism When Behaviorism is Beneficial for Learners Teacher directed instruction Basic skill acquistion Automaticity of Math facts Drill and practice Classroom management Positive reinforcement When Cognitivism is Beneficial for Learners Problem solving Reasoning Guided learning Scaffolding Collaborative groups Modeling When Constructivism is Beneficial for Learners Advanced knowledge Group projects Hands on exploration Class discussions Experiments Research projects • Behaviorism • Lesson Plan: “Seven Fat Cats” (Utah LessonPlans, 2003) • Teacher reads “Seven Fat Cats” • Students identify rhyming words Learning Theory – Lesson Plan Lesson Plan for “Seven Fat Cats” (Utah LessonPlans, 2003) Behaviorism • Teacher directed instruction • Teacher directed activities • Basic rhyming skills • Sound matching • Drill and practice • Cognitivism Lesson Plan in Cognitivism Add brain storming map Students identify additional rhyming words Follow up activity Collaborative groups Rhyming word fill in Group discussion Share collaborative group work • Behaviorism or Cognitivism Behaviorism or Cognitivism for Lesson Plan Cognitivism Begin with original lesson Expand lesson: include Cognitivism components Encourages Student involvement Reasoning and thinking skills Cooperative learning skills • Wiggins Backward Design Wiggins Backward Design Identify desired results • Individualizes instruction for audience • Ensures instruction is viable Acceptable evidence for assessment Verifies learning occurs Plans learning and instruction Hones and drives writing of instruction • Strengths and Limitations Strengths of Wiggins Theory Identifies desired results Goals and objectives Established before writing instruction Ensures instruction addresses goals and objectives Identifies assessment process Tailors and directs instruction Planning instruction Maximizes effective learning Limitations of Wiggins State standards Big idea might not include all standards Goals Subject to vagueness Student feedback None required Strengths of Gagne’s Events Gaining attention Engages brain activity Objectives Prepares learner Prior learning Builds on established brain pathways Learner guidance and feedback Encourages students Limitations of Gagne’s Events Instructional planning No step included in model for planning Nine step model Lengthy Laborious Strengths of Teaching for Understanding Generative topics Correlates to students’ interests Understanding goals Can span over a school year Performance of understanding Students demonstrate new knowledge Assessment is ongoing Designer can begin in any order Weaknesses of Teaching for Understanding Design is not extraordinarily structured Guidelines are vague Learner audience More suitable for upper grades • Gagne’s Design Gagne’s Design Engages learners Catches attention Directs instruction by objectives Prepares learners Provides learner guidance Necessary for young learners Elicits practice Crucial for acquisition of basic skills References Utah LessonPlans. (2003, August 8). Seven Fat Cats. Retrieved from http://www.uen.org/Lessonplan/preview.cgi?LPid =5640