Lang exam Reading Q4
advertisement

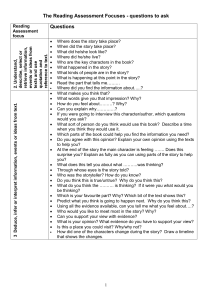
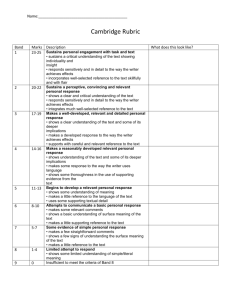
Section A - Reading Question 4: Language Comparison Approaching and answering Question 4 Question 4: Language Comparison •16 marks •25 minutes •You need to COMPARE OR CONTRAST 3 or 4 devices (techniques, or features) used in two texts •Analyse the effect of some of these devices; comment on similarities and differences of the two texts Language devices used by non-fiction writers. Which can we recall? In a different colour, suggest a typical effect of these devices. Hint: Think about Question 2 Common linguistic devices • 1st, 2nd or 3rd person (narrative viewpoint) • Directly addressing the reader • Imperatives • Rhetorical questions • Register - Formal/Informal language • Diction - Simple/Complex vocabulary • Figurative Language & Imagery: Similes/Metaphor/ Personification etc. • Word play & puns • Alliteration • • • • • • • • • • • • • Rhyme & Rhythm Anecdote & Allusion Slogan & Catchphrase Statistics & Facts Exaggeration & Hyperbole Repetition Humour Lists Emotive language Punctuation type Expert advice Short sentences Superlatives How is language used for effect? Language is always used for some kind of effect or other. Often, without commenting on specific linguistic devices, you can talk about the kind of language a writer uses, noticing what kind of words are used, or what kind of tone or style is created by language and structure. Look at these examples… The writer uses dramatic and violent language in order to describe the horror of the attack at the end of the extract. Phrases like “chill horror”, “sudden fear” and “thunderous crack” portray the fear and terror experienced by the Indians who are attacked. Powerful words such as “war”, “huge” and “ruining” emphasise and perhaps exaggerate the seriousness of the issue. The writer uses a chatty, informal tone, using contractions like “I’m” “don’t” and “can’t”. Language is highly descriptive, with adjectives such as “golden” and “spectacular” conveying the writer’s appreciation for his surroundings. Some common linguistic devices. What are they? Example “According to UK government calculations, 214 of the most senior eurocrats get paid more than David Cameron's £178,000 a year.” “Human lives are nothing but a series of unfortunate upgrades. Yes, even yours.” “Starbucks wakes up and smells the stench of tax avoidance controversy” “Who's opposing the benefit cap? Who's calling for a ringfence of council tax benefits for families in need? Who's arguing to maintain the child tax credit threshold? Who's fighting against families being rehoused miles away from their children's school? Who's calling for more social housing?” “The ferry was packed with buses, petrol tanks, vans, land cruisers, jeeps, fuel tankers, cars – and people.” Name of Language Device(s) Some common linguistic devices. What are they? Example Name of Language Device(s) “According to UK government calculations, 214 of the most senior eurocrats get paid more than David Cameron's £178,000 a year.” “Human lives are nothing but a series of unfortunate upgrades. Yes, even yours.” “Starbucks wakes up and smells the stench of tax avoidance controversy” “Who's opposing the benefit cap? Who's calling for a ringfence of council tax benefits for families in need? Who's arguing to maintain the child tax credit threshold? Who's fighting against families being rehoused miles away from their children's school? Who's calling for more social housing?” “The ferry was packed with buses, petrol tanks, vans, land cruisers, jeeps, fuel tankers, cars – and people.” Look out for: statistics and figures, directly addressing the reader, repetition, alliteration, personification, sibilance, lists, rhetorical questions, humour, exaggeration… 2. Compare the different ways in which language is used for effect in the two texts. Give some examples and analyse what the effects are. •Actively read the text: You are looking for particular parts of the text where language creates a certain effect, and serves the purpose of the article (e.g. to inform, persuade or describe). •The language question is always the same: It will ask you to compare Text 3 (or ‘Source 3’) with either Text 1 or Text 2. •Highlight words, phrases, passages, statistics etc. that will help you answer the question. •You might like to annotate the texts very briefly with ideas that will help you answer the question. 3. Writing up ideas •Now you’re ready to write up your ideas •Compare how language is used for effect in one of the texts, and then the other in each paragraph. Conclude by giving reasons for similarities / differences. •Pepper your points with short quotes which give examples of how language is used for effect. They need to be analysed, as you need to suggest how these effects are created by the writers. IN PAIRS 3. Connective Firstly Secondly Thirdly As well as this Furthermore Moreover Finally Lastly Likewise Similarly Unlike As well as In contrast to The author / language in the text… advises argues builds connotes contrasts conveys creates demonstrates describes depicts emphasises evokes exaggerates gives the impression gives a sense highlights informs Implies Indicates Juxtaposes Narrates Persuades Realises Recognises Refers to Reflects Represents Reveals Signifies Suggests Symbolises Shows Tells The reader… (or ‘we’…) Is made aware Is informed Is told Is shocked / fascinated / persuaded / made to sympathise etc. Learns Discovers Realises USEFUL WORDS & PHRASES Compare the different ways in which language is used for effect in Everest the Hard Way and Rafting on the Grand Canyon. Give some examples and analyse what the effects are. ON YOUR OWN Question 4: Language Comparison – Sample Mark Scheme