The Endocrine System
advertisement

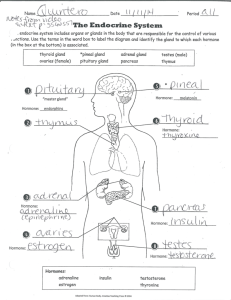
The Endocrine System Body Control System Endocrine Combining form crin/o means secrete Prefix endo means within Endocrine System consists of glands that secrete Function of Endocrine System Hormones are the chemical messengers for the Endocrine System Produce and secrete hormones into blood stream to help control body activities Works closely with the Nervous System Exocrine Glands Exocrine Glands – secrete their products into ducts The ducts then carry the secretions into body cavities or to body surface E.g. sweat glands, sebaceous glands, lymph glands Endocrine Glands Don’t contain ducts Secrete their products directly into the blood stream E.g. Pituitary gland, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal, pancreas, ovaries, testes What are hormones? Chemical messengers Transfer information and instructions from one set of body cells to another Each type of hormone stimulates a specific sets of cells in organs to cause an action of that organ to happen E.g. oestrogen causes changes to female sex characteristics helps maintain homeostasis of the body Endocrine Glands Endocrine Gland Hormones secreted Function Pituitary gland “master gland” many e.g. thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) Human Growth Hormone (HGH) stimulates secretion form thyroid Thyroid Thyroxine Thyroxine controls body metabolism Parathyroids parathyroid hormones (PTH) regulates calcium and phosphorus in blood corticosteroids adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinepherine) many e.g. anti-inflammatory, affect CNS in stress response Pineal Gland Melatonin Seratonin Exact function unknown but influences sleep & onset of puberty Pancreas is both an exocrine gland & endocrine Insulin Control blood sugar levels Gonads i.e. testes, ovaries Oestrogen, progesterone testosterone Development of sex characteristics Adrenal glands 1.Adrenal cortex 2.Medulla Stimulates cell growth throughout body Word Components Gland Root word combining form Hormone Disorder Pituitary gland Pituita,pituitar FSH (follicle stimulating hormone); LH (leutinising hormone); HGH (human growth hormone); ACTH (adrenocorticotrophic hormone); ADH (antidiuretic hormone) Hypersecretion – gigantism, acromegaly Hyposecretion – Dwarfism,acromicria Hyposecretion of ADH – diabetes insipidus Thyroid gland Thyr, thyr/o thyroxine Hyperthyroidism – Graves Disease Hypothyroidism – Goitre Parathyroid Parathyr, parathyr/o Parathyroid hormone for calcium function in bones and nervous system Hyperparathyroidism – bone softeneing Hyperthyroidism – twitching Word Components Gland Root word combining form Hormone Disorder Adrenal Adren,adren/o Adrenaline, cortisol & helps body cope with stress Hypersecretion – Cushing’s syndrome Hyposecretion – Addison’s disease Pancreas Panreat, pancreat/o Insulin Hyperglycaemia High blood sugar levels (Daibetes) Hypoglycaemia Low sugar levels Word parts aden/o gland adriano adrenocortic/o andr/o -crine end/o -globulin glyc/o Ket/o -micria Natr/i adrenal gland adrenal cortex male to secrete within protein sugar Ketones Condition of small size sodium Word parts -plasia condition of growth progest/o -ptosis -trophic -tropic progesterone falling / prolapse pertaining to nourishment stimulating Abbreviations BSL Blood sugar level BSS Blood sugar series FBSL Fasting blood sugar level GTT Glucose tolerance test HRT Hormone replacement therapy Diabetes DiabetesType I IDDM (Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus) Pancreas doesn’t make insulin Diabetes Type II Inadequate insulin NIDDM (Non Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus)