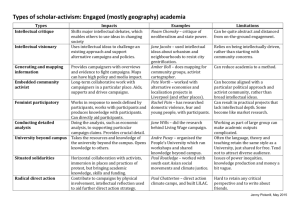
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT- AN EMERGING DISCIPLINE
advertisement
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT- AN EMERGING DISCIPLINE B.V.L.NARAYANA Sr Professor (T M ) RSC/BRC INTRODUCTION THOUGHTS ON KNOWLEDGE – Have roots in philosophy, religion– thought at abstract level – In work place settings—action and thought – At intellectual level– intellectual capital– action-thought-dynamism linked to performance—more explicitisation of efforts – Increasing use of technology, research History Knowledge management –old issue – Philosophical roots and industrial – Implicit and unsystematic, not integrated Presently oriented towards commercial success Present emphasis due to realization that – Consider the whole person to manage knowledge— integrate motivation, attitudes, cognition – Evolution towards personal and intellectual freedom and rise of importance of knowledge workers—social movements started 200 years ago – Industrial revolution , increased pace of economic growth – Evolved to KM and emphasis on explicitisation Kinds of KM Three levels – Strategic –application, distribution of knowledge for business enterprise viability – Tactical- IM and IT focus, intellectual asset focustechnology driven – Operational –people focus, emphasize utilization to improve performance Should be seen as the systematic and explicit management of knowledge related activities, practices, programmes, and policies within the enterprise to ensure enterprise viability Effectiveness of KM An effective KM initiative is indicated by – – – – Does not lead to more work Leads to less work, more efficiency Are part of pre-existing and ongoing efforts Removes fear of sharing knowledge; increases status of experts – Promotes increased individual learning – Defines terms crisply – Leverages existing knowledge for enterprise effectiveness Driving forces of KM External forces – Rapid Advances in technologies – Globalization of business • Increased opportunities and competition – Sophistication of customers- increasing demands, and changing preferences – Sophisticated competitors – Sophisticated suppliers Driving forces of KM Internal forces – Bottle necks to enterprise effectiveness – Increased technological capabilities – Need to understand human cognitive functions Ongoing forces – – – – – – Economics of ideas—innovation ICT and information management Understandings in cognitive sciences Shifts in bottle necks Customization requirements globalization Impact of KM in organizations New perspectives and activities Market value is now equated to management of intellectual capital Need to manage IC Explicit, deliberate and systematic efforts at KM Efforts integrate theoretical and abstract perspectives – Linkage to how people reason, think and take decisions, learning theory Future of KM Insights into personal and intimate knowledge Future practices will be purposeful, explicit, systematic and driven by technology Spread of experiences of KM implementation Facilitating management practices towards KM Embedding of KM perspectives in regular activities Introduction of complimentary work teams and virtual organizations Increasing explicitisation of personal knowledge KM practices will become norms Matching of expert systems and networks to learning styles Increasing role of artificial intelligence Impact on work practices Firm level- expertise on managing IC Middle management level- importance of managing local investments in and coordination and application of knowledge assets to meet operational objectives KM level –enterprise level coordination and facilitation KM operational level –hands on capabilities to obtain, organize, store, retrieve and use knowledge Enterprise level –new ways of working Anticipated changes at work place Relative frequency of work Target for intelligent automation Targets for intelligent automation Routine work made simpler( simple repetitive and well understood) potentials for delivering work requiring greater knowledge 1 Unchanged work Logical or less common variations-Transformati ons of routine situations Complex but expected extensions of known routines integrated with external factors Potential for delivering work requiring greater knowledge2 Unexpected challenges but with a mix of routines and external factors Potential for delivering work due to knowledge3 Totally unexpected situations and non routine challenges yet within larger job scope Potential for knowledge based work Unusal challenges outside job scope Increasing complexity of knowledge intensive and other work Final thoughts KM must – Justify its existence—financially – Be Performance related – Have a strategic perspective – Improve efficiency – Reduce and ease methods of working ATTITUDES habits ACTIONS skills Knowledge Data and information ANY QUESTIONS