Young children growing, thinking, and learning
advertisement

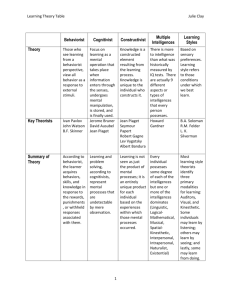
Young children growing, thinking, and learning Focus Questions What is DAP? What are five major theories of development? What patterns make up physical, social, emotional, and intellectual development? How can knowledge about child development affect curriculum planning, identifying special needs, and understanding the relationship of diversity? Developmentally Appropriate Practices (DAP) Age Appropriate Early Childhood = birth to age eight Individually Appropriate Theories of Development • • • • • Behaviorist Maturationist Constructivist Social Learning Ecological Systems Theory Behaviorist Stimulus Response Theory Reinforcements Positive Negative Punishments Operant conditioning Extinguishing behavior Maturationist Theroy “Unfolding of development” Experience play less important role Child’s developmental level most important determiner of social and intellectual success Constructivist Theory Jean Piaget Assimilation Equilibrium Equilibration Lev Vygotsky Social-cultural influences Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) Multiple Intelligences Theory Howard Gardner Nine Intelligences Linguistic Logical-mathematical Spatial Bodily-kinesthetic Musical Interpersonal Intrapersonal Naturalist Extstentialist Social Learning Theory Albert Bandura Social Learning Theory Modeling Ecological Systems Theory Urie Bronfenbrenner Child develops through compels systems of relationships Cultural environments Cultural milieu Not static, but dynamic Theoretical Influences on Teacher Planning Implementation of instruction Theoretical Influences on observations Provide different Points of view Children’s Development Physical Social Emotional Intellectual Patterns of Physical Development Movements become organized into patterns Growth is cephalocaudal (proceeds from head to toe) Growth is proximodistal (proceeds from center of the body outward) Rate of development is vaiable and related to environmental factors ( nutrition, freedom to practice, etc) Patterns of social Development Personality Self-Esteem Role of Play Social Relationships Aggression Sex- Role Identification Erikson’s Stages of Psychological Development in Children Basic Trust vs. Mistrust Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt Imitative vs. Guilt Industry vs. Inferiority Patterns of Intellectual Development Vygotsky Inersubjectivity Scaffolding Make – Believe Piaget Brain Research Sensorimotor Preoperational Concrete Operational Theories Imaging techniques Brain becomes “wired” Child Development and Curriculum Planning Children with Special Needs Observe development Seek programs as needed Celebrating Diversity Development must be viewed within framework of culture Impact of language within culture Impact of motor control encouraged within culture Teachers must be sensitive to cultural expectations