Stratified Sampling
advertisement
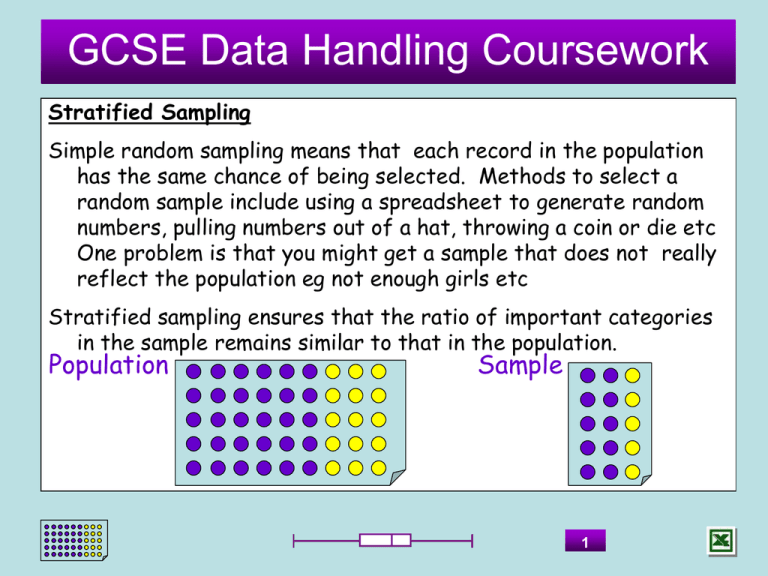
GCSE Data Handling Coursework Stratified Sampling Simple random sampling means that each record in the population has the same chance of being selected. Methods to select a random sample include using a spreadsheet to generate random numbers, pulling numbers out of a hat, throwing a coin or die etc One problem is that you might get a sample that does not really reflect the population eg not enough girls etc Stratified sampling ensures that the ratio of important categories in the sample remains similar to that in the population. Population Sample 1 GCSE Data Handling Coursework Stratified Sampling (Part1) Eg The Exams Board would like a sample from four schools of maths coursework. They would like a sample of 50 pupils. Look at the table below. How many pupils should each school provide? School Pupils A 315 B 123 C 95 D 217 Answer Total Pupils =315+123+95+217=750 A 315 x 50 = 21 pupils 750 B 123 x 50 = 8.2 ie 8 pupils 750 C 95 x 50 = 6.33 ie 6 pupils 750 D 217 x 50 = 14.5 ie 15 pupils 750 For a random stratified sample 21 pupils should be picked at random from school A, 8 from B etc 2 GCSE Data Handling Coursework Stratified Sampling (Part2) Eg The Exams Board would now like a 50 strong sample from 4 schools that’s representative of the male/female breakdown. How many males/females should each school provide? (Use the school sample from Part 1) Answer Total Pupils = 750 School A F M 150 165 Pupils A 21 150 x 21 = 10 females 11 males 315 B8 61 x 8 = 4 females 4 males 123 C6 60 x 6 = 4 females 2 males 95 D 15 122 x 15 = 8 females 7 males 217 315 B 61 62 123 C 60 35 95 D 122 95 217 For a random stratified sample 10 female & 11 male pupils should be picked at random from school A, etc 3