Medieval Culture: Architecture, Literature, Learning & Science
advertisement

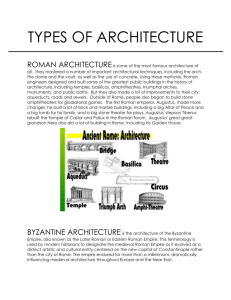
Ch. 4 Sec. 2 Medieval Culture Flowering of Medieval Culture due to: • Expansion of trade and commerce • Rise of wealthy class/bourgeoisie • Importance of education and the arts Importance of Religion • Cathedrals built to glorify god, art and the people • Took years to complete • Expensive to build • Dominated the skyline and life in towns and cities Architectural Types: • Romanesque – Early 1000’s – Influenced by Roman architecture – Rounded arches and domed roof – Outside walls thick – Small windows • Gothic – 1050 - 1300 – Tall, light, airy – Flying butress support weight of the roof – Walls thin, higher and windowed – Tall arches Romanesque Gothic Literature: • Vernacular – Languages of the regions developed • British, German, Scandinavia based on German • France, Italian, Spain strongly influenced by Latin • Troubadours spread the use of vernacular languages – Chanson de geste or a long narrative poem ‘Song of Roland’ • Fables: humorous poems mocking nobles • Dante ‘Divine Comedy’ (Dante and Virgil talk to great historical figures such as Homer about Hell, Purgatory and Heaven) written in Italian vernacular so it could be read by many • G. Chaucer ‘Canterbury Tales’, talks about lives of ordinary people! Centers of Learning: • Churches, monastaries, Cathedrals • Towns attracted scholars – Universities: group of scholars and students – Eventually came under the control of the church – Had to obtain official charters – Often officials were members of the church • Student interests protected • Excluded women • Trained for positions in the church and universities • Few comforts, cold, few manuscripts Revival of Classical Knowledge • Roman Law • Aristotle’s system of knowledge relied on ‘reason’. This conflicted with the teachings of the church which were based on faith. • ‘Scholasticism’ – used reason and logic to support Christian beliefs. – Thomas Aquinas - ability to reason was a gift of God ; if differences exist its caused by mistaken reasoning. Science and Technology • Church was the authority, no scientific reasoning • Arabic numerals, lead to new mathematics • Plow windmill, clock flying butress, glass • Roger Bacon: noted importance of experiments Medieval Medicine • • • • • • Relied on folk medicine Traditional remedies Superstition Christian beliefs Evil spirits pilgrimages