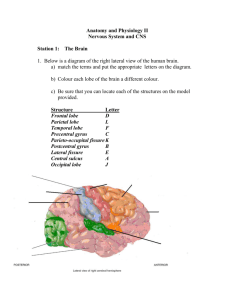
Brain Functional Areas: Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital Lobes
advertisement

. سهل هللا له به طريقا ً إلى الجنة،ًمن سلك طريقا ً يلتمس به علما Functional areas of Frontal lobe. Frontal Eye Field. Motor Speech Area of Broca Premotor Area (6) مهمة (44,45) (Area 8) مهمة part Inferior frontal gyrus. Precentral gyrus Anterior to primary motor Posterior middle frontal Found in the dominant area Extends to anterior part of gyrus. paracentral lobule on medial Posterior parts of superior, middle hemisphere (left). and inferior frontal gyri. side. 1. Initiation of movement of the 1. Successful performance Conjugate Sequence of contraction of opposite half of the body. of voluntary motor movements of the speech muscles. 2. 40% of pyramidal fibers activities initiated in Area eyes. arise from there. 4 حركة العين المزدوجة 2. (Program, design, plan and store programs of motor activities ) 3. Inhibit muscle tone. 1. Hemiplegia. (spastic paralysis 1. Apraxia (Inability to do Loss of conjugate 1. Expressive or motor of the extremities of the skilled voluntary motor aphasia. (in ability to movements of the opposite half of the body. actions. produce proper speech.) eyes. 2. Masticatory, laryngeal, 2. Spasticity of muscles. 2. Patient finds difficulty to Pharyngeal, upper facial and express what he wants to extraocular muscles not say with right words. 3. Patient can understand paralyzed as the bilaterally represented. other’s speech. Comparsion Primary motor Area (4) مهمة Site Function Lesion Prefrontal area (area 9,10,11 and 12) Anterior parts of the three frontal gyri. Responsible for Emotions (, Ideas and personality. دي الناصية اللي هي مصدر .المشاعر واالفكار والصدق والكذب )(ناصية كاذبة خاطئة Motor homunculus: In the motor area of the cerebrum, the human body is represented upside down, as uppermost part controls the feet and the lowermost part controls the head, neck, face, and fingers. The body representation of different parts of body within the cortical areas depends on skill, not the size of this part (the parts with the skilled movements occupy larger areas as hands) . سهل هللا له به طريقا ً إلى الجنة،ًمن سلك طريقا ً يلتمس به علما Comparsion Primary Sensory Area (3,1 and 2) Site Postcentral gyrus Function Lesion Functional Areas of Parietal lobe. Sensory Association Area (5 and 7) Sensory Speech Area of Wernicke. Superior parietal lobule. Posterior part of superior temporal gyrus. Angular and supramarginal gyri. Found in the left dominant hemisphere. Receives all general sensation from Recognizing the objects placed in Understanding speech. opposite half of the body. hand without seeing it. (stereognosis). Loss of all sensation from the opposite Asterognosis. Receptive aphasia: Inability to understand spoken or written speech. half of the body. Sensory homunculus: In the sensory area of the cerebrum, the human body is represented upside down, i.e. uppermost part controls the feet and the lowermost part controls the head, neck, face, and fingers. The body representation of different parts of body within the cortical areas depends on the sensitivity, not the size of this part (tongue and hand have large areas, while the back has small area) Functional Areas of Temporal Lobe (mainly audition) Comparsion Primary Auditory Area (41,42) Auditory association area (22) Primary Olfactory center Site Superior surface of superior temporal Lateral surface of superior Uncus. gyrus (Heschl’s gyrus) temporal gyrus. Function Lesion Perception of sounds from both ears Recognition and interpretation of Perception of smell sensation. from the opposite side. the sounds. يعنيepitpecrep الحظ ان البرايماري بيبقا لل Decrease in hearing but not deafness. .فقط الشعور Cochleae are bilaterally presented, so .االسوسييشن بيكون لتميز وترجمة الشعور والمحفز lesion in one cortex doesn’t cause unilateral deafness. Olfactory association center (28) Anterior part of parahippocampal gyrus. Recognition of odors. . سهل هللا له به طريقا ً إلى الجنة،ًمن سلك طريقا ً يلتمس به علما Functional Areas of lttrerccO Lobe (mainly vision) Comparsion Primary visual area/ Striate area (17) Secondary Visual Area (18 and 19) Site Medial surface of occipital lobe. Adjacent to the primary visual area. Above and below the postcalcarine sulcus. Function Lesion Gustatory center (43) Insula. Recognition and interpretation of the visual Recognition of the tasted materials. images. Lead to blindness in the corresponding part of visual Failure of interpretation and recognition of field to both eyes. visual images. يعني لو المكان دا اتصاب مثال فالفص االيمن هيخلي فيه عمى في النص .الشمال للعينتين دا مش علينا بس للمعرفة يعني منapprcpeerc وبيحصل مرض اسمه : وفيه بيكون رؤية المريض كدا،عندي كدا Perception of Vision.