D07_Named_Pipes
advertisement

Named Pipes
Kinds of IPC
Mutexes/Conditional Variables/Semaphores
Pipes
Named
pipes
Signals
Shared
memory
Messages
Sockets
Named Pipes
A pipe
is a unidirectional buffer between two
processes handled by the kernel
A pipe has a file descriptor, just like a file
Unnamed pipes can only be used between
processes with a common ancestor
Named
pipes do not require any relationship
Named pipes are special files within the file system
you can use ‘ls’ and see them
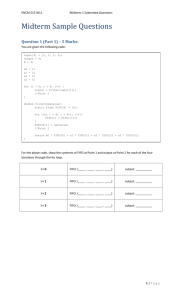
Creating a FIFO
– Library function called mkfifo()
Synopsis
C
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
Creating a FIFO file
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
if(access("my_fifo",F_OK) == 0)
cout << "FIFO already exists" << endl;
else {
int res = mkfifo("my_fifo", 0777);
if (res==0) cout << "FIFO created" << endl;
else cout << "FIFO not created" << endl;
}
}
Working with FIFOs
use
open and close as with ”normal” files
both
ends of the pipe need to be opened!
Note: open returns a file descriptor
A process
opening a name pipe blocks until some
process opens the FIFO at "the other end"
close
doesn’t need to block
A reading
reader
process blocks if the FIFO is empty
and writer become synchronized
Opening a FIFO pipe file
Named
pipes are opened like other files
For example, by using the open system call
flags specify whether to read or write, and whether to block
Opening
a FIFO with the O_NONBLOCK flag makes
access to the pipe non-blocking:
for O_READ, open returns immediately
even if the writing end has not been opened by another process
for O_WRITE, open returns immediately, but returns -1 if the
reading end is not open
Also subsequent read and write operations become nonblocking!
Reading and writing to FIFOs
Like
normal files
using low-level I/O: open, read, write, close
using high level C++ I/O: <fstream>
For
FIFOs in blocking mode
reading from an empty fifo blocks
writing to a full FIFO blocks
size of FIFO buffer PIPE_BUF = 4096 KB
For
FIFOs opened with O_NONBLOCK
reading from an empty FIFO succeeds with 0 bytes of data
writing to a full or nearly full FIFO may fail, or may write only
some of the data into the FIFO