ses2 - Dr. McLaughlin`s Classes
advertisement

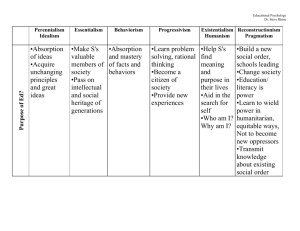
Curriculum Philosophy Session Two PLANNING CURRICULUN FOR THE FUTURE IS DIFFICULUT • MANY THINGS EED TO BE CONSIDERED • WHAT PHILOSOPHY • WHAT APPROACH AND HOW DO YOU DECIDE ON THE MATERIAL Philosophy • Many believe that Curriculum is the foundation of education. • A philosophy is the foundation of a curriculum, You need to know what you believe in before you can formulate a curriculum Philosophy • Underneath almost everything we feel strongly about, we have a philosophy – Coaches- blitzing defenses, speed, power, a system versus star talent, – Relationships- there are certain beliefs people have as a must in a partner, it varies from person to person – Building a curriculum is no different Philosophy related to curriculum • Philosophy is central to curriculum • A philosophy of a particular school or district influence the goals, content and organization of its curriculum • Philosophy provides a framework for organizing schools and classrooms, it establishes: – What schools are for, processes to be used, and activities that schools should emphasize Philosophy related to curriculum • People that are divided in philosophy can rarely work together in close proximity for long periods of time • An ideal curriculum workers have a philosophy that hopefully can be can be adjusted or modified as new best practices and information becomes available Try and Determine Yours • What parts of the following philosophies do you feel matches your thinking? There are Four Major Philosophies • • • • • Idealism Realism Pragmatist Existentialism You saw a brief introduction of these, based on their names, write some basic tenets that you feel would apply to these philosophies based on their title. (Do in a group, one philosophy per group) Idealism • Plato is the father of Idealism • Others include Froebel ( kindergarten), Ralph Waldo Emerson, Theory Thoreau • It is the search of truth and enduring values, • Truth is more than physical senses, it is a mental process Idealism • In education, this means • Teachers should be teaching conceptual matters • Relating concepts to one another • Most important subjects are the most abstract-philosophy, theology, mathematics then history and literature also language • at the bottom is science- based only on senses and facts, not on pure thought Realism • Created to Aristotle and Thomas Aquinas • Realist view the world in terms of objects and matter • people come to know the world through their senses and their reason • Everything is derived from nature and is subject to its laws Realism • In education • They have similar beliefs as far as course structure, believe in separate course for everything, feel abstract courses at the top of the educational food chain • However, they also value the sciences • The three Rs are a basic component Pragmatist • Pragmatist believe in change and relativism • The truth is always changing, there is not anyone single universal truth • Believed in testing, looking for answers as important • Supported by William James, John Dewey Pragmatist • In education, • Problem solving is important • Teaching is more exploratory than explanatory: method more important than subject matter Existentialist • In existentialism, people constantly make choices and through these define themselves • We are what we choose and by our choices we define ourselves • Individualism is important • Primarily developed from Europe Existentialist • In education, the existentialist stress personal fulfillment- they believe the most important knowledge is that of the human condition • Schools should provide choices for students to pursue their personal growth • Schools curriculum should provided experiences and subjects that lend themselves to individual freedom and choice – Ex. Arts, drama, literature music filmmaking, – They illustrate emotions, feelings and insight Existentialist • Critics of existentialism, feel that it is impossible to achieve the goals of existentialist in school because schools are all about socializing students to be similar, it is about conformity and institutionalization Activity • In your groups look at each of the four philosophies, what implication would hat have when planning a curriculum • What are some features you would see in district that followed one of these philosophies? Educational Philosophies • Out of these four major philosophies four educational philosophies have grown out of these. They are: – Perennialsim – Essentilsim – Progressiveism – Reconstrcutionism Perennialism • • • • The oldest and most conservative philosophy Derived from realism Dominated much of American curriculum In elementary school: – pushes the three Rs – Moral and religious training • In secondary: – Latin, Greek, grammar logic and geometry Perennialism • It stress traditional values • It teaches knowledge that has been thought for years • The reason is, a person’s function in society is the same today as it always was, why teach them differently? The aim is as it always was • The goal is to develop the rational person, uncover universal truths by developing a student's intellect and moral character Perennialism • The curriculum is subject centered • It is logically organized and emphasizes language, literature mathematics and science • Stimulates discussion and student's rational powers • Lessons are taught using the Socratic method, oral expression, and lecture Perennialism • • • • The curriculum has little time for electives Little time for vocational training Character education is important Some types of education still feel that this is the most effective way to build a curriculum and teach students- it is a rite if passage • Law school, medical schools Perennialism • Permanent studies is an example of Perennialism • When students read and discuss great works of the past in order to cultivate their intellect • It is considered broad based and a means to cultivate the mind • Ex include reading, Plato, Aristotle, Shakespeare Perennialism • The Paideia Proposal a book written by Adler, proposed three types of learning to improve the intellect – Organizational knowledge to be taught by didactic instruction – Basic learning skills- taught through coaching and presentation – Acquisition of values- to be taught by the Socratic method Perennialism • The Paideia Proposal does not present any subject matter as an end in itself- you do not learn algebra to become a mathematician, you learn math to develop intellectual skills • Advocates for a universal curriculum • All students get the same subjects with high quality teaching Perennialism • Allan Bloom feels that recent changes in our curriculum that focus on “cultural relativism”, quick fixes and “trivial pursuits” has degrade American education • He feels that we fail to develop critical thinking skills • He feels that a good old liberal Arts education is the answer to this Perennialism • Supporters of Perennialism such as Charles Murray, feel that the west Western world) and America once were the best and brightest and made significant contribution in all academic areas • He now feels we are no longer the best and feels that part of the solution to become the best again is a move toward the Perennial curriculum College curriculum have done this: How are they different? • Bachelor of Science • Bachelor of Arts Essentialism • A traditional philosophy- started in 1930’s became famous in 1950-60s ( after Sputnik) • In elementary school focus on three Rs • Secondary education is aimed at five subject areas: – – – – – English Math Science World Language History Essentialism • In Essentialism Secondary education devalues subject areas such as : • Home economics • Music • Art • Physical education • Art They feel they are frivolous and a waste of money but begrudgingly allow a few students to take them Essentialism • Essentialist value – – – – knowledge acquisition Facts Conceptual though Problem solving • Essentialist feel all students should follow the same curriculum- its pace should be adjusted according to the needs of the students • Emphasis is placed on Science, math and new technologies Essentialism • Essentialist feel that taking a student’s interest or social issues into account is wasteful • Teaching methods that rely on psychological theories are also wasteful • The teacher is a master of the course content and subject matter and a model worth emulation • The teacher is the authority, decides on the curriculum and exhibits high standards- the teacher needs to be respected. Essentialism • The Essentialist view is reflected in the “A Nation at Risk Report” and the NCLB law in a more moderate form (Not far enough for essentialist) Essentialism • Much of what we see today aligns with the essentialist philosophy – Standards. Statewide testing, standards before moving to another level ( in 13 states) • Provide bonuses to school, teachers and principals that achieve • Teachers standards-With this push for standards- came the push to have Teacher standards Essentialism • Teachers standards-Many states added competency testing for beginning teachers ( 40 states) • A heavy emphasis has been placed on reading writing ( about two hours a day) • Math ( about one hour a day • Curriculum has become aligned with high stakes tests and has reduced electives Essentialism • Although this push for standards seems basic, in some areas experts can not agree on what they should be • Also essentialist feel that pure information is not stressed enough- facts such as acid rain and bay of Biscay, allows for greater understanding because of background knowledge and facilitates communication Progressivism • Is a contemporary curriculum philosophy based on john Dewey’s beliefs. • Focus is on schools nurturing cooperation, self discipline • Since needs change constantly, no need to focus on a fixed body of knowledge • Focuses on How to think and not what to think Progressivism • • • • Activities are key to instruction Constructivist methods Interdisciplinary Teachers are the leader of groups facilitating activities • Students ad teachers plan activities together • Teachers help students locate, evaluate analyze and interpret the data ( from activities) Progressivism • Progressives reject rote learning, recitation and textbook authority, corporal punishment • The focus is on the learner and not the subject • There were radical progressives groups on either side- progressive extremist and lazierfaire- one side devalued knowledge and the other devalued adult authority over children Progressivism • Relevant Curriculum- Although most followers of the progressive philosophy have lost prominence, the desire for relevant curriculum survived • Instruction should be associated from life experiences, students should be motivated and interested Progressivism • Other aspects: – Individualization – Extend curriculum beyond the school ( work study programs- internships) – Electives and mini-courses – Courses that interest students- music through rap Progressivism The Humanistic perspective- this curriculum push was a reaction to the hard-line repressive curriculum that isolated students ( Perennialism and existentialism) Builds on Maslow’s work and looks at affective outcomes rather than cognitive The goal is to produce self actualized peopledevelop the whole person Progressivism The Humanistic perspectiveSome people feel this way now They feel we overemphasize the cognitive, put lots of pressure on students do away with Humanist seek more meaningful relationships between students and teachers Progressivism • Eventually many educational leaders that believed in the Progressive philosophy called for a radical school reform • The felt that teachers disliked and distrusted their students • The considered schools highly discriminatory – The felt schools sort children for different jobs and perpetuated class differences Progressivism • Many of these educational theorist had nothing good to say about how schools run and how teachers operate • Some of their comments include – Elem schools are babysitting – Successful students are strategist in a game to beat the system – Some called for eliminating schools Reconstructionism • This philosophy evolved out of disgruntled progressiveist • They felt that society was going to pot and that education was the best way to achieve social reform • Developed originally in 1920’s • The felt the progressiveist overemphasized child-centered education and ignored social needs of all classes Reconstructionism • Felt the students and teachers must improve society • Felt teachers and classrooms should NOT be politically neutral felt that teachers and students need to take a stand on issues • Need to develop well reasoned students that can communicate well Reconstructionism • Curriculum should be based on social issues • School programs would include – Examine society cultural heritage – Examine controversial issues – be committed to bringing about constructivist social change – Cultivate future oriented attitudes – Enlist students and teachers to enhance educational opportunities for all children. Reconstructionism • A branch of reconstructivism, was a group that felt improving our social conditions was not enough. The Internationalist, felt that schools need to address issues on an international scale • Internationalist will speak of such things as – The global village, global interdependence, the shrinking world, greenhouse effect Reconstructionism • Internationalist feel school need to teach students to understand various global systems and would build the curriculum around them • Such concepts as global: – political, economic, physical resources, cultural issues, and communication – World problems such as Western imperialism, Arab Nationalism and the growing economic influence of China and India Reconstructionism • Reconceptualist view the technical approach to curriculum as too narrow and feel it is not sensitive enough to people’s feelings • Our society today is marked bay a failure to accommodate diversity and indifference to people's needs • They are socially sensitive and concerned with broad problems of society Reconstructionism • Reconceptualist value communication skills , art poetry, dance , drama, literature, psychology and ethics • Feels that schools have oppressed that poor and we need to design a curriculum to free them Reconstructionism • The final branch of reconstructivism, is the Equal Educational opportunity • Their goals is to assure that children born in any class have the same opportunity as children in any other class • Schools represent the means to achieve goals • Currently this does not happen because education is so closely tied to social class and family background Reconstructionism • The Equal Educational opportunity followers admit that upper ward mobility is possible in the current system and would be less if it were not for public schools Reconstructionism • The Equal Educational opportunity followers believe in the following five factors relevant to equal /unequal educational opportunities: – – – – Offering the same curriculum to all children School’s racial composition equality of teacher morale and teacher expectations Cognitive an economic outcomes for students with equal backgrounds and abilities – Cognitive and economic outcomes for students with unequal backgrounds and abilities Reconstructionism • The Equal Educational opportunity followers believe in the following five factors relevant to equal /unequal educational opportunities: – – – – Offering the same curriculum to all children School’s racial composition equality of teacher morale and teacher expectations Cognitive an economic outcomes for students with equal backgrounds and abilities – Cognitive and economic outcomes for students with unequal backgrounds and abilities Activity – Based on these four principles, what tenets do you personally hold as valuable in your curriculum Philosophy.