Workshop_CNRCWP_17au18Dec2013
advertisement

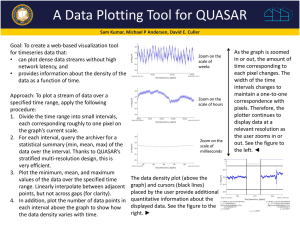
Canadian Network for Regional Climate and Weather Processes Practical Training: Plotting Model outputs using Matlab: Time series, vertical profiles, 2D plot Contact: oumarou.nikiema@uqam.ca nikiema@sca.uqam.ca Bureau: PK 6425 Model output Configuration In practice, model data are in 5D format: Variable of interest: temperature, Wind, … Valid Time Vertical position: pressure (hPa), height (m), … Latitude position Longitude position Example: TT(2005010103,500hPa,30°N,60°W) Login to the Computer … Access to Skynet3: ssh -Y wh01@skynet3.sca.uqam.ca Copy the directory in your home: cp –r /home/nikiema/Workshop_CNRCWP ./ Enter into the work directory: cd Workshop_CNRCWP Check the list of files in your directory: ls –al Open Matlab: matlab& Data files used by Matlab programs In Directory: /skynet3_exec2/nikiema/Data_Workshop 3 files: (Use VOIR to check these informations) • Model output: dp_... 2005-01-01-03 to 2005-02-01-00 each 3h Var.: TT , UU, VV and GZ 26 pressure levels • Era-Interim data: era-… 2005-01-01-03 to 2005-02-01-00 each 6h Var.: TT , UU, VV and GZ 34 pressure levels • LoLa: latitude and longitude information Data files used by Matlab programs voir -iment « Filename » -style | more Example: IP1: Pressure code CMC time code IP2: forecast hours ? For instance: IP2=1 for one hour prevision Data files used by Matlab programs voir -iment « NOM DE FICHIER » –style Exemple: IP2: 30*24+3=723 Initial date: 2004-11-01-00h GZ data on: 2004-12-01-03h Conversion: RPN to binary format Getfld6.m to Matlab function used to convert RPN binary fromat Getfld6.m: works only with E32 format It is possible to change data format by using: r.diag repack … Sometimes, you need to uncompress the data by using: fstuncompress -fstin « input file » -fstout « output file » Conversion: RPN to binary format Getfld6.m: to Syntax: Matlab function used to convert RPN binary fromat Conversion: RPN to binary format TYPVAR: type de variable; 'A'(analysis),'P'(forecast),'X' NOMVAR: variable name: TT, UU, VV, GZ, … ETIKET: name of simulation DATE: CMC date code r.date -Sn 2005062600 (Code de la date: 324252800) 1 janv. 1900 0h ===> 010100000 1 janv. 1900 1h ===> 010100010 IP1: level code IP2: prevision time IP3: 0 Useful Fortran programs … r.date –Sn options : Example: Result: Result: -n -S -L -V « DATE » to add end of line character, to get CMC time stamp (time code), to get date in this form YYYY MM DD HH MM SS to get in this form YYYYMMDDHHMMSS00 Useful Fortran programs … r.ip1 -kn options : NB: « PRESSION » 2 -n to add end of line character, -k to get height code knowing the level in hPa, m, … -o to get the level value (in hPa, m, …) knowing code k =====> kind kind : level type (the number express the level unity) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 : m [metres] (height with respect to sea level) : sg [sigma] (0.0 ----> 1.0) : mb [mbars] (pressure in millibars) : [others] (arbitrary code) : M [metres] (height with respect to ground level) : hy [hybrid] (0.0 ----> 1.0) : th [theta] Useful Fortran programs … r.ip1 -kn options : Examples: Result: Result: « PRESSION » 2 -n to add end of line character, -k to get height code knowing the level in hPa, m, … -o to get the level value (in hPa, m, …) knowing code 2. 1D plot of the Vertical profile Script: Vertical_Profile_1D.m 2. 1D plot of the time series Script: Time_series_1D.m 3. 2D plot: Latitude-height cross section Script: Vertical_Profile_2D_Along_long_v1.m 3. 2D plot: Latitude-height cross section Sometimes, it is better to plot the cross section With Log of the pressure. Script: Vertical_Profile_2D_Along_long_v2.m 3. 2D plot: Vertical profile of zonal-mean Temperature Script: Vertical_Profile_2D_Zavg.m 3. 2D plot: Longitude-height cross section Script: Vertical_Profile_2D_Along_lat_v2.m 4. 2D plot: horizontal map of temperature 4. 2D plot: horizontal map of temperature quiverm ==> to see wind vectors There are too much vectors, so you have to reduce the numbers of vectors Ouvrir et exécuter: Visu_vent2D_2.m 5. Comparison: Model vs Era-Interim 1D vertical profile of the domaine-averaged 5. Comparison: Model vs Era-Interim Time series plot of the domaine-averaged 5. Comparison: Model vs Era-Interim