Literary Elements Slide Show
advertisement

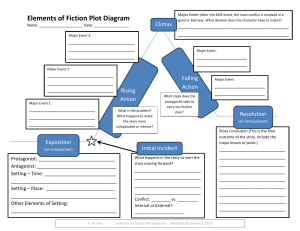
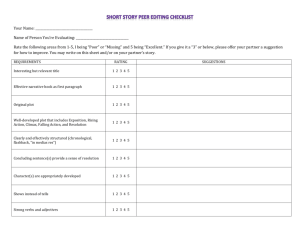
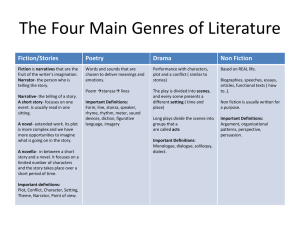
What is a story? As the following statements are read aloud, stamp your feet for the statements that you think do • My shoes are tied • Once, there were 3 raccoons and a skunk on my porch • The beach is beautiful • My name is Cori • My cat escaped through the window this summer not suggest a story. PLOT: The series of events that create the basic situation Somebody Wanted But So What is PLOT? Plot is the literary element that describes the structure of a story. The plot is all of the related events in the story that make-up the basic situation from beginning to end. Plot Components Climax: the turning point, the most intense moment—either mentally or in action: when you discover at last how the conflict ends Rising Action: the series of attempts the character makes to try to solve the problem Falling Action: all of the action which follows the climax Exposition: the start of the story, the situation before the action starts: meet the characters and establish the setting Resolution: the conclusion, the tying together of all of the threads Types of Linear Plots Plots can be told in Chronological order flashback In media res (in the middle of things) when the story starts in the middle of the action without exposition Setting • Where and when a story takes place. • Sometimes, we must guess the location or time period of a story from contextual clues, because the author does not tell us. – anachronism: a detail of a story that does not fit the setting • A computer in a Shakespearean tragedy would be out of place. Mood • Overall feeling of a story. (Ex. Happy, sad, depressing, scary) Character: A person or animal that takes part in the action. This includes the main character, called the protagonist. Types of Characters: Protagonist: Main character Antagonist: the opposing character or force to the protagonist Static characters (flat): Characters who do not change within the context of the story. Characters we don’t get to know very well. minor characters . Dynamic characters (round): Characters who change, grow, or develop within the context of the story. Characters we get to know well. We know their fears, fantasies, history, etc. Characterization Authors reveal a character’s personality and motivation by what they THINK, FEEL, SAY, and DO 1) Appearance: How does a character look and dress—what does this reveal about the character? 2) Personality: Is the character emotional or rational—shy or outgoing—skillful or clumsy— happy or depressed—caring or cold—honest or dishonest? 3) Background: Where and how did the character grow up—what is the social status of the character—how have they been educated—hobbies or skills—what do they do for a living? 4) Motivation: What does the character want? What are the character’s wishes, desires, dreams,and needs? 5) Relationships: How is the character related to the other characters and how do they interact with each other? 6) Change: Does the character change in the course of the narrative? Does he or she learn or grow? In other words, is the character static (unchanging) or dynamic (changing)? Conflict Conflict is the dramatic struggle between two forces in a story. Without conflict, there is no plot. Types of Conflict External Conflict character vs character character vs. nature character vs. society character vs. supernatural character vs. technology Internal Conflict character vs. self Theme The message or moral the author is trying to convey about society or just a truth of life. Usually suggested by characters’ thoughts or what the main character learns. “Bugs” The lightning bug has wings of gold, The goldbug wings of flame; The bedbug has no wings at all, But it gets there just the same. Point of View: The perspective from which the story is told First Person = When a story is told from the perspective of one of the characters in the story. Uses the pronoun “I.” Third Person When a story is told from the perspective of someone outside the story looking in. Third person limited: perspective is limited to what one character does, observes, or thinks. (He, she, it) Third person omniscient: the story is told from the perspective of someone who knows and sees all (he, she, it) Flashback An interruption of story action to tell about something that happened earlier. Foreshadowing Hints of clues in a story about what is to come. Genre: a category of artistic, musical, or literary composition characterized by a particular style, form, or content. • • • • • • There are 5 major forms genres of literature: Plays Non-fiction (autobiography, biography) Fiction (fantasy, historical fiction, magic realism, mystery, science fiction, realistic fiction, Western) Poetry Folk tale or classic