A way of predicting population changes
AGE STRUCTURE DIAGRAMS
POPULATION STRUCTURE
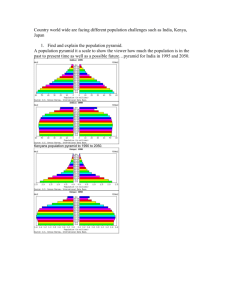
The population pyramid displays the age
and sex structure of a country or given area
Population in
Five Year
Age bands
MALES
To the left
Usually, but not always,
In % to make for easier
comparisons
between countries
FEMALES
To the right
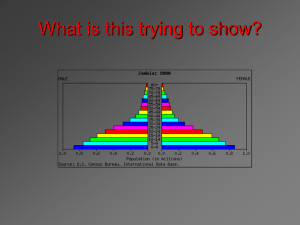
What Population Pyramids Show Us
Economically
More
Developed
Country
Economically
Less
Developed
Country
KEY
slope of pyramid indicate the death rate
width of the base is related to birth rate/fertility rate
proportions of men and women can suggest male or female migrations
height of graph can indicate life expectancy (ignore the very thin end of the
wedge as occurs on graph B as these people are a definite minority)
"kinks" indicate dramatic reductions in birth rate or increases in
death rate in the past
area of graph indicates total population - compare areas of different
population age groups or different sex on one graph
The overall shape of the population pyramid can indicate whether it is an
Economically More Developed Country or Economically Less Developed Country
Population pyramid of a less developed
nation (broad base population pyramid)
Population Pyramid of Nigeria (1995)
Importance of Population Pyramids
A BROAD BASE POPULATION
PYRAMID MEANS A COUNTRY SHOULD:
•increase food production
•build more homes & schools
•plan for more job opportunities for the young in future
•implement birth control program/campaigns
•Usually agricultural population with problems of overpopulation.
Population pyramid of a developed nation
Population Pyramid of Sweden (1995)
Importance of Population Pyramids
A NARROW BASED POPULATION
PYRAMID MEANS:
Birth rate and Death rate low so a country may need to:
•Work out incentives to encourage more births
•Begin hiring foreign labor
•Ensure proper medical services & health care for the aged
Age Structure Diagrams
Male
Female
Rapid Growth
Guatemala
Nigeria
Saudi Arabia
Ages 0-14
Slow Growth
United States
Australia
Canada
Ages 15-44
Zero Growth
Spain
Austria
Greece
Negative Growth
Germany
Bulgaria
Sweden
Ages 45-85+
Predict the future population change for each of the three age structure diagrams
U.S. Population by age 1900, 2000, and 2050 projected
Population
structure by
age and sex in
developed and
developing
countries.
Tracking the baby-boom generation in the
U.S.
THOMAS ROBERT MALTHUS
1766-1834
Growth Potential of
Subsistence Vs. Population
TIME 1
140
TIME 2
120
TIME 3
100
TIME 4
80
60
TIME 5
40
TME 7
20
TIME 6
0
SUBSISTENCE
POPULATION
TIME 7
Basic Point From MALTHUS:
Population and food supply (subsistence) grow at
different rates
Population will outgrow food supply
Results from the point of crisis include famine
and war
What are advantages and disadvantages of
reducing births: Controversy
Can the world’s resources
support an additional 2.5
billion by 2050?
Is the Earth
overpopulated?
Carrying capacity
If yes, what should be
done?
What is a sustainable
population?