Compass Rose
advertisement
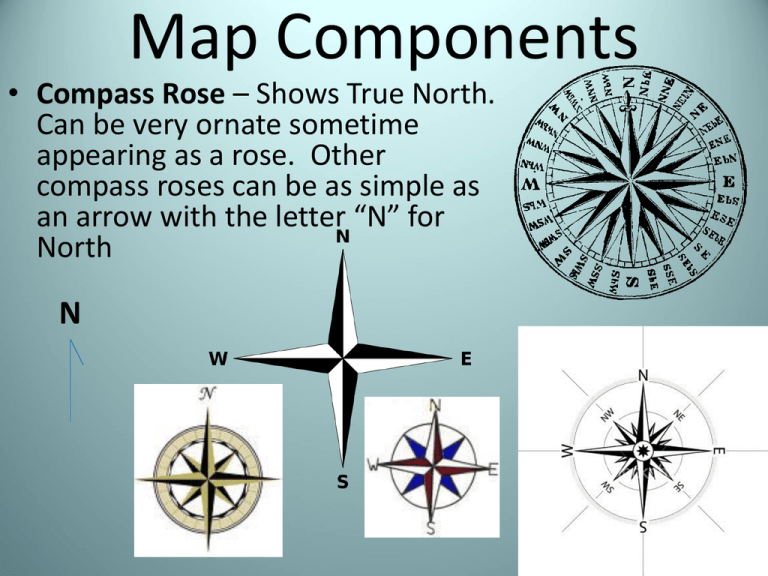
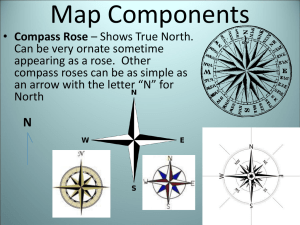
Map Components • Compass Rose – Shows True North. Can be very ornate sometime appearing as a rose. Other compass roses can be as simple as an arrow with the letter “N” for North N WHERE ARE THE COMPASS ROSES? IS THIS MAP WRONG? Why do most maps have Africa centered? • The Prime Meridian is actually centered on Greenwich, England • Scientist from an English observatory first conceptualized the grid system • Legends / Keys – are symbols used to explain the multiple features of a map. Scale – Converts comparative distance from actual measurement to one corresponding the much smaller map. Scales will often show distance converting miles and kilometers (KM). Latitude – (Also called PARALLELS) are imaginary lines on a map going east and west. These lines are used for measuring distances NORTH and SOUTH of the EQUATOR. These lines measure 90 degrees north and south of the equator (there are 180 degrees total). High Latitudes Arctic Circle 66 1/2°N Mid Latitudes Tropic of Cancer 23 1/2°N Low Latitudes Equator 0 degrees Tropic of Capricorn 23 1/2°S Mid Latitudes High Latitudes Antarctic Circle 66 1/2°S Latitudes 90 ° High Latitudes 60 ° Not about top and bottom, it’s about the number of the latitude degree Mid Latitudes 30 ° If it is a large number of degree (60-90) it will be high latitudes. Low Latitudes AKA Tropics If it is a small degree (0-30 it will be low latitudes. 30 ° Mid Latitudes 60 ° High Latitudes 90 ° Longitude – (Also called Meridians) are imaginary lines on a map passing through the north and south poles. These lines are used for measuring distances EAST and WEST of the PRIME MERIDIAN. These lines measure 180 degrees west and east of the Primer Meridian (there are 360 degrees total). Hemisphere – divides the Earth into two halves. The Prime Meridian divides the Earth into a Eastern and Western hemisphere and the Equator divides the Earth into a Northern and Southern hemisphere. Grid System – series of intersecting lines of Latitude and Longitude on a map used for plotting Absolute Location. Two ways to get Absolute Location 1. Potting Latitude and Longitude 2. Address Location – Where something is • Relative Location – Where is something in relationship to something else. – Example: My window is across the street from Subway. • Can you find that on a map? • Absolute Location – There is no question about where it is. It can be “pen pointed.” – Example • Address • Plotting Latitude and Longitude. 0 LOSERS 10 20 30 40 50 40 30 20 10 0 EAGLES SOUTH 50 40 30 20 10 0 10 20 30 40 50 NORTH LOSERS EAGLES 10 20 30 40 10 20 30 40 50 EAST WEST 10 20 30 40 50 40 30 20 10 0 50 GRID SYSTEM NORTH 20 10 0 10 20 0 A S 20 20 10 10 T E 0 S 10 E 10 20 20 W 20 10 0 10 SOUTH 20 T GRID SYSTEM 20 10 0 10 20 20 20 0 0 10 10 20 20 10 10 20 10 0 10 20 A – 60 degrees North, 90 degrees West B – 0 degrees, 150 degrees West C – 30 degrees South, 60 West D – 60 degrees South, 60 degrees East E – 30 degrees North, 150 degrees East F – 50 degrees North, 70 degrees East You will have a freehand World Map Quiz (spelling will count) on the date listed on the board. The following will be required: • Grid system – Label degrees of Latitude in increments of 30 – Label degrees of Longitude increments of 60. • Continents (label all 7 ) • Oceans (label all four) • Compass rose • Legend / Key (continent, grid) • • • • • • • • Equator Prime Meridian International Dateline Tropic of Cancer 23 1/2°N Tropic of Capricorn23 1/2°S Arctic Circle 66 1/2°N Antarctic Circle 66 1/2° S Scale (10° Longitude = 70miles)