File
advertisement
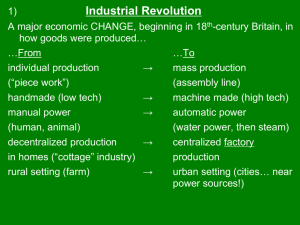
Industrial Revolution Major Inventions of the 18-19th centuries Spinning Jenny Spinning Jenny Invented by: James Hargreaves Description: Allowed more thread to be produced by spinners Impact: Spinning process FASTER Water-powered loom Water-powered loom Developed by: Edmund Cartwright Impact: Weavers could keep pace with the surplus of yarn produced by new spinning machines Steam engine Steam engine Improved by: James Watt Description: Made changes that enabled engine to drive factory machinery Impact: Railroad industry booms; Factories can be built AWAY from WATER Railroad Railroad Description: A steam locomotive that ran on rails Impact: Helped lay foundations for larger markets (Transportation) and opened up new forms of investment Paddle-wheel Steamboat Paddle-wheel Steamboat Built by: Robert Fulton Impact: Transportation along canals, rivers, and lakes made easier Industrial Societies What makes an industrial society? Do the benefits of industrialization justify the costs? The Second Industrial Revolution 1870-1914 New Industrial Frontiers • Steel, Chemicals, Electricity • 1870-1914: Steel replaced iron • Steel: Lighter, smaller, faster machines, engines, railroads, etc. • Electricity: Convertible into heat, light, motion • New transportation: ocean liners, airplanes, automobiles 2 New Economic Zones • Industrial – Makes Stuff • Agricultural – Grows Stuff Go to the map on p. 617 Attempts at Reform LABOR UNIONS • Formed by laborers to work for change • Unions negotiate for better pay, conditions with employers • 1st Legal Strikes in GB in 1870s • Union goals – higher wages – shorter hours – improved conditions Universal Education • Causes – 2nd Ind Rev needed skilled workers – To better educate voters – To build Patriotism • Effects – Need more Teacher, so more Colleges – Increased Literacy, so more Newspapers Socialism Ideology • Equality of all people • Upset with elites (bankers, industrialists,etc) • Replace competition w/ cooperation • Early socialists: “Utopians” • Ultimate goal: classless society Marxist Socialism A system in which society, usually in the form of the government, owns and controls the means of production (nat. resources, factories, etc.) Karl Marx: “World history… is the history of class struggles.” Marx’s Theory • Industrialized societies split into two great classes • Oppressors vs. Oppressed • Struggle leads to violent revolution • Dictatorship: gov. in which a person or group has absolute power • Final Revolution Classless society Key Terms Bourgeoisie The Middle Class French origin; Sometimes negative connotation— Ambition, greed Proletariat The Working class; From Marx’s theory (i.e. Russian Revolution) Industrial Capitalism Economic system based on industrial production Produced middle class; people who built factories, bought machines, studied markets