Chordate Quiz: Evolution, Anatomy, and Physiology
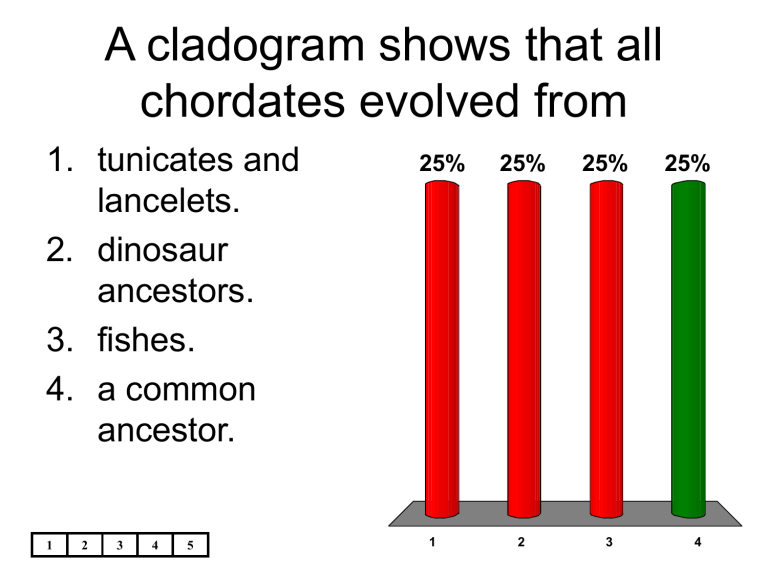
A cladogram shows that all chordates evolved from
1. tunicates and lancelets.
2. dinosaur ancestors.
3. fishes.
4. a common ancestor.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Pikaia was an early
1. worm.
2. fish.
3. chordate.
4. lancelet.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
A flexible, supporting structure found only in chordates is the
1. nerve net.
2. notochord.
3. pharyngeal slits.
4. dorsal fin.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Vertebrae are characteristic of
1. worms.
2. all chordates.
3. vertebrates only.
4. reptiles only.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Which of the following animals is
NOT a nonvertebrate chordate?
1. Pikaia
2. worm
3. lancelet
4. tunicate
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Which of the following pairs of modern chordate groups contains the most closely related groups?
1. hagfishes and lungfishes
2. lampreys and rayfinned fishes
3. birds and crocodilians
25% 25% 25% 25%
4. sharks and the coelacanth
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Convergent evolution is the process that produces
1.
species that are similar in appearance and behavior but not closely related.
2.
unrelated species that are different in appearance and behavior.
3.
closely related species that are similar in appearance and behavior.
4.
closely related species that are different in appearance and behavior.
25%
1
25%
2
25%
3
25%
4
1 2 3 4 5
The sugar glider is an Australian marsupial. The eastern flying squirrel is a North American placental mammal. Both animals are nocturnal, live in trees, and can glide through the air using a flap of skin that stretches between the legs on each side of the body. The resemblance between these two animals is an example of
1. oviparous 25% 25% 25% 25% development.
2. ectothermy.
3. chordate diversity.
4. convergent evolution.
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
A rapid growth in the diversity of a group of organisms as they adapt to new conditions is called a(an)
1. cladogram.
25% 25% 25% 25%
2. ecological condition.
3. adaptive radiation.
4. evolutionary history.
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
The largest living group of chordates is the
1. amphibians.
2. fishes.
3. mammals.
4. birds.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Compared with the number of extinct chordate species, the number of living chordate species is
1. much larger.
25% 25% 25% 25%
2. slightly larger.
3. the same.
4. much smaller.
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Essential life functions are carried out most efficiently when an animal’s internal body temperature is
1. insulated.
25% 25% 25% 25%
2. regulated by the environment.
3. the same as its external temperature.
4. within a particular
“operating range.”
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
In vertebrates, each of the following is important in regulating body temperature
EXCEPT a
1. source of heat.
25% 25% 25% 25%
2. way of conserving heat.
3. long digestive tract.
4. method of eliminating heat.
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Suppose a terrestrial vertebrate has an optimal body temperature of 37 °C but lives in an environment where the air temperature is 40 °C. Which of the following is the most important requirement for that vertebrate to control its body temperature?
25%
1.
conserving body heat
25% 25% 25%
2.
eliminating excess body heat
3.
maintaining a high, steady production of body heat
4.
absorbing heat easily from its environment
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Which of the following help mammals retain body heat?
1. hair and sweat glands
2. hair and body fat
3. bones and sweat glands
4. bones and body fat
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Panting is a behavior that is seen most often in
1.
endotherms that need to cool down.
2.
endotherms that need to warm up.
3.
ectotherms that need to warm up.
4.
ectotherms that are at their ideal body temperature.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
If each of the following vertebrates had a body temperature of 37 °C and was placed in a cage where the air temperature was 30 °C, which vertebrate would have the lowest rate of heat exchange with the air?
1. a hamster
25% 25% 25% 25%
2. a lizard
3. a frog
4. a snake
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
The main difference between ectotherms and endotherms is
1.
the source of their body heat.
2.
how they obtain food to provide for their metabolism.
3.
whether they control their body temperature.
4.
whether they conserve or eliminate body heat.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Filter feeders include all of the following EXCEPT
1. lancelets.
2. flamingoes.
3. crocodiles.
4. baleen whales.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Raccoons are omnivores, which means that they eat both meat and plant material. If you compared the digestive tract of a raccoon with that of a similar-sized herbivore and a similarsized carnivore, the raccoon’s digestive tract would most likely
25% 25% 25% 25%
1.
be the shortest of the three.
2.
be the longest of the three.
3.
have a length intermediate between the herbivore and the carnivore.
4.
be the same length as the other two.
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Colonies of bacteria in the intestines of a cow are helpful in
1. digesting cellulose fibers.
2. producing enzymes that digest meat.
3. straining plankton from water.
4. tearing and slicing food.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Which of the following vertebrates has a heart with four chambers?
1. a salamander
2. a lizard
3. a goldfish
4. a cow
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
What is the general rule regarding respiratory organs in chordates?
1.
Aquatic chordates use lungs, and land vertebrates use gills.
2.
Aquatic chordates use lungs and gills, and land vertebrates use gills.
3.
Aquatic chordates use gills, and land vertebrates use lungs.
4.
Aquatic chordates use gills, and land vertebrates use lungs and gills.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Chordate respiratory structures include all of the following EXCEPT
1. simple air sacs.
2. the medulla oblongata.
3. the surface of the skin.
4. the lining of the mouth.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
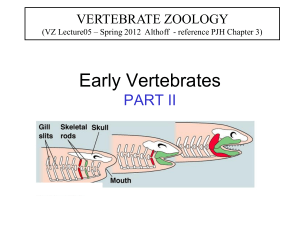
When a fish respires, water flows in through which of the following patterns?
1.
in through the gill slits, over the gill filaments, and out through the mouth
25%
2.
in through the gill filaments, over the gill slits, and out through the mouth
3.
in through the mouth, over the gill slits, and out through the gill filaments
4.
in through the mouth, over the gill filaments, and out through the gill slits
1
25%
2
25%
3
25%
4
1 2 3 4 5
Which of the following happens in the alveoli?
1.
Oxygen diffuses into the blood, and carbon dioxide diffuses into the air.
2.
Carbon dioxide diffuses into the blood, and oxygen diffuses into the air.
25%
3.
Both oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse into the blood.
4.
Both oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse into the air.
1
25%
2
25%
3
25%
4
1 2 3 4 5
The main difference between an amphibian lung and a reptilian lung is that
1.
an amphibian lung has a greater surface area for gas exchange.
2.
a reptilian lung has a greater surface area for gas exchange.
3.
an amphibian lung contains thousands of alveoli, but a reptilian lung does not.
4.
a reptilian lung is connected to air sacs, but an amphibian lung is not.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
The most efficient vertebrate lungs are found in
1. amphibians.
2. reptiles.
3. birds.
4. mammals.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Adult frogs breathe by using all of the following EXCEPT
1. their gills.
2. their moist skin.
3. their lungs.
4. the lining of their mouth and pharynx.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
In a single-loop circulatory system, the atrium
1. receives the blood from the body.
2. pumps blood to the gills.
3. pumps blood to the lungs.
4. pumps blood throughout the entire body.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
A single-loop circulatory system is characteristic of
1. fishes.
2. amphibians.
3. most reptiles.
4. crocodilians.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
If a vertebrate has a circulatory system that carries oxygen-rich blood directly from the heart to the muscles, that vertebrate could be a
1. bony fish.
2. cartilaginous fish.
3. larval amphibian.
4. mammal.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
The heart of a fish has
1. one atrium and one ventricle.
2. one atrium and two ventricles.
3. two atria and one ventricle.
4. two atria and two ventricles.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Ammonia is excreted by all of the following EXCEPT
1. larval amphibians.
2. tunicates.
3. most reptiles.
4. most fishes.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Animal X excretes nitrogenous wastes as uric acid and has a well-developed cerebrum. Animal X is a
1. cartilaginous fish.
25% 25% 25% 25%
2. crocodilian.
3. mammal.
4. bird.
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
In tunicates, some nitrogenous wastes leave the body in the form of
1. urea.
2. ammonia.
3. uric acid.
4. protein.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Suppose a mammal is born with a defect in its medulla oblongata. Which of the following functions is most likely to be affected?
1. ability to detect odors
2. ability to analyze objects by sight
3. control of the lungs, heart, or digestive tract
4. conscious thought
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
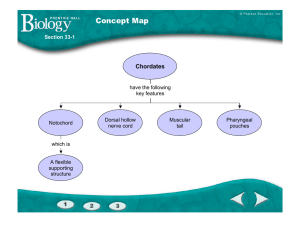
The simplest chordates that have cephalization as adults are
1. lancelets.
2. fishes.
3. amphibians.
4. reptiles.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
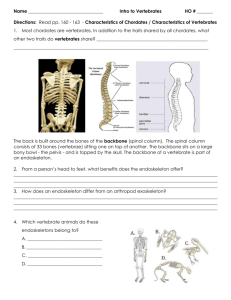
All chordates have
1. a bony skeleton.
2. pharyngeal pouches.
3. a backbone.
4. fin girdles or limb girdles.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
When a fish swims by bending its body and tail from side to side, the swimming movement is produced mainly by the contraction of muscles located in
25% 25% 25% 25%
1.
limbs that stick out sideways from the body.
2.
limbs that are attached straight under the body.
3.
a siphon through which water leaves the body.
4.
blocks on either side of the backbone.
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
A function of ligaments in a backbone is to
1.
generate forward thrust during swimming.
2.
keep the backbone straight and rigid.
3.
connect the vertebrae.
4.
make the body bend back and forth.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
The sets of bones that support the limbs of vertebrates are called
1. opercula.
2. limb girdles.
3. ligaments.
4. vertebrae.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Sexual reproduction occurs in
1. fishes.
2. amphibians.
3. mammals.
4. all of the above
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Embryos obtain nutrients from the yolk inside the egg in
1. oviparous and ovoviviparous animals.
2. viviparous and ovoviviparous animals.
3. viviparous and oviparous animals.
4. viviparous animals only.
25% 25% 25% 25%
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Reproduction in most mammals involves
1.
internal fertilization and ovoviviparous development.
2.
internal fertilization and viviparous development.
3.
external fertilization and oviparous development.
4.
external fertilization and either oviparous or ovoviviparous development.
25%
1
25%
2
25%
3
25%
4
1 2 3 4 5
The notochord is a supporting structure that is found only in chordates.
_________________________
1. True
50% 50%
2. False
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
The simplest living animals to have all four chordate characteristics are the larvae of frogs. _________________________
1. True
50% 50%
2. False
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
In a cladogram of modern chordates, endothermy is the adaptation that separates reptiles, birds, and mammals from other chordate groups.
_________________________
50% 50%
1. True
2. False
1 2 3 4 5 1 2
The ability of birds and bats to fly is an example of convergent evolution.
_________________________
1. True
50% 50%
2. False
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
More than 90 percent of all chordates living today are vertebrates.
_________________________
1. True
50% 50%
2. False
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
The largest group of chordates is the fishes. _________________________
1. True
2. False
50% 50%
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
The ability of a vertebrate to regulate its body temperature is especially important in a habitat where the temperature remains constant throughout the year.
_________________________
1. True
50% 50%
2. False
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
A vertebrate that has a low rate of metabolism and a body that is not well insulated is probably an endotherm. _________________________
1. True
2. False
50% 50%
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
Animals that control their body temperatures from within are called ectotherms.
_________________________
1. True
50% 50%
2. False
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
Endotherms generate their body heat by metabolic activity.
_________________________
1. True
50% 50%
2. False
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
The surface area of the lungs increases as you move from amphibians to mammals.
_________________________
1. True
50% 50%
2. False
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
The only reptiles that have four-chambered hearts are snakes.
_________________________
1. True
50% 50%
2. False
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
Chordates in which eggs develop outside the body are called viviparous.
_________________________
1. True
50% 50%
2. False
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
If a vertebrate has a four-chambered heart and excretes nitrogenous wastes as urea, that vertebrate is most likely a bird. _________________________
1. True
2. False
50% 50%
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
Internal fertilization and viviparous development are characteristics of most mammals. _________________________
1. True
50% 50%
2. False
1 2 3 4 5
1 2
0
0
0
0
0
Participant Scores
Participant 1
Participant 2
Participant 3
Participant 4
Participant 5
The chordate family tree has its roots in ancestors that vertebrates share with tunicates and ____________________.
1 2 3
If the fossil record indicates that the number of species in a particular group of animals increased sharply during a given period, that group probably underwent
________________________ at that time.
1 2 3
One example of ____________________ evolution is provided by penguins and seals, both of which hunt in the ocean and have streamlined bodies and flipperlike appendages.
1 2 3
In environments in which temperatures are high and fairly constant most of the time, ____________________ is a more energy-efficient method of controlling body temperature.
1 2 3
A(An) ____________________ is an animal whose body temperature is controlled mainly by the transfer of heat between its body and its surroundings.
1 2 3
An animal that strains small pieces of food from the water is called a(an)
____________________.
1 2 3
In a vertebrate with lungs, the ____________________ functions as a passageway through which air enters and leaves the lungs.
1 2 3
In a mammalian lung, gas exchange occurs inside bubblelike structures called
____________________.
1 2 3
In the lungs of a(an) ____________________, gas-exchange surfaces are always in contact with air that contains much oxygen.
1 2 3
In a frog, the heart chamber that contains blood with the highest concentration of oxygen is the ____________________.
1 2 3
If an animal has a four-chambered heart, it has a(an) ____________________-loop circulatory system.
1 2 3
Aquatic amphibians and most fishes excrete nitrogenous wastes in the form of
____________________.
1 2 3
The region of your brain that you use to determine the answers to test questions is the ____________________.
1 2 3
A bird cannot fly with a badly damaged
____________________, because this part of the brain controls a bird’s sense of balance and movement.
1 2 3
Animals whose embryos obtain nutrition directly from the mother’s body are said to have
____________________ development.
1 2 3
Identify four features common to all chordates.
1 2 3
The oxygen concentration on one side of a gill membrane
(side A) is 0.05 percent. The oxygen concentration on the other side of the gill membrane (side B) is 0.5 percent. In which direction will oxygen molecules move?
1 2 3
If two extinct but unrelated species of chordates shared many adaptations, what could you infer about the ecological conditions those species encountered?
1 2 3
List three features that are included in the ways in which all vertebrates control their body temperature.
1 2 3
Some species of fish that live in the Arctic Ocean will die if the water temperature exceeds 10 °C. This temperature is called the lethal temperature for that species. How would the lethal temperature of a related species of fish that lives in tropical waters compare to the lethal temperature of the Arctic species?
1 2 3
Why is it advantageous for birds to use feathers instead of body fat as a primary means of insulation?
1 2 3
Animals A and B are terrestrial vertebrates of the same size. One is an ectotherm, and the other is an endotherm. The resting metabolic rate of animal A is five times that of animal B. Using this information, state which animal is the ectotherm and briefly explain your decision.
1 2 3
Why is it illogical to say that the simple organ systems of a tunicate must be inferior to the organ systems of a mammal?
1 2 3
In what ways other than length do the digestive tracts of carnivores and herbivores differ?
1 2 3
The goosefish is a sluggish, bottom-living fish. The mackerel is a highly active, fast-swimming fish. If you compared the gill surface area in these two fishes, after adjusting for the fishes’ body size, what would you expect to find?
1 2 3
How are the alveoli in a mammalian lung analogous to the folds in a mammalian cerebrum?
1 2 3
Describe the basic pathways of the two loops in a double-loop circulatory system.
1 2 3
List two functions of vertebrate kidneys.
1 2 3
Describe the functions of the optic lobes and olfactory bulbs in a vertebrate brain.
1 2 3
Contrast movement in larval and adult tunicates.
1 2 3
Suppose you are studying two species of chordates that share a particular adaptation. What would you need to know to determine whether this sharing was the result of convergent evolution?
1 2 3
Why is the control of body temperature important for vertebrates?
1 2 3
Describe two hypotheses concerning the evolution of endothermy in vertebrates. What does the evidence on this issue suggest?
1 2 3
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of being an endotherm and an ectotherm in an environment where the air temperature drops to an average of 5 °C during the winter.
1 2 3
The basic features of temperature control in a house are a furnace; insulation in the walls, floor, and ceiling; and one or more doors and windows that open to the outside. Describe the analogous features in an endotherm and explain their roles in temperature control.
1 2 3
The skin of most amphibians is richly supplied with capillaries. The skin of most reptiles, in contrast, does not have such a dense network of capillaries. Explain the functional importance of this difference.
1 2 3
Contrast the respiratory systems of mammals and birds.
1 2 3
Describe the major differences among the chambers of the heart in the five main groups of vertebrates.
1 2 3
In a mammalian heart, how does the total volume of blood that the right ventricle pumps in one hour compare with the total volume that the left ventricle pumps during the same period? Explain your reasoning
1 2 3
Describe the forms in which nitrogenous wastes are eliminated in different groups of chordates.
1 2 3