Review PowerPoint
advertisement
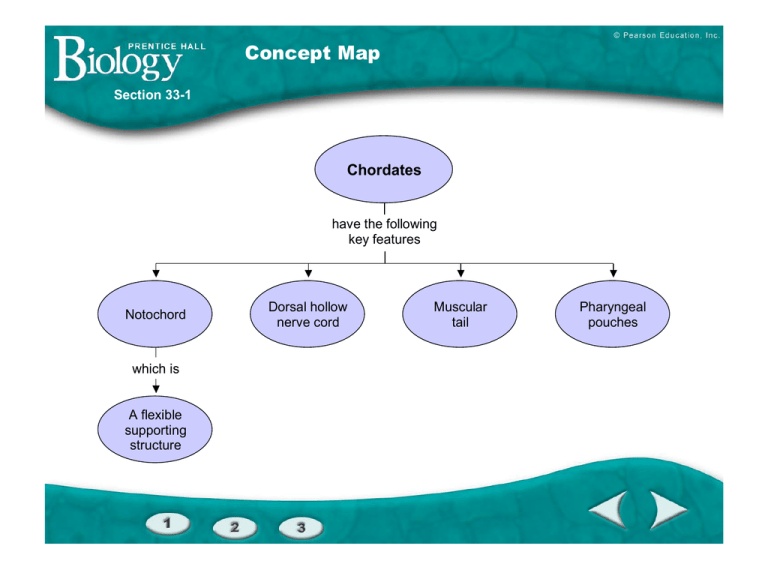
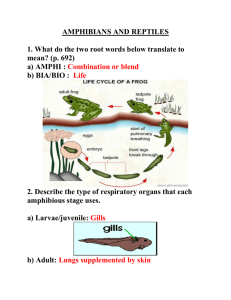
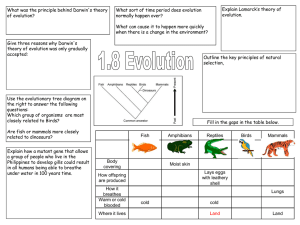
Concept Map Section 33-1 Concept Map Chordates have the following key features Notochord which is A flexible supporting structure Dorsal hollow nerve cord Muscular tail Pharyngeal pouches Section 33-1 Nonvertebrate chordates Jawless fishes Cartilaginous fishes Bony fishes Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals Figure 33–2 A Cladogram of Chordates Body Temperature (°C) Environmental Temperature (°C) Comparing Functions of Chordates Function Nonvertebrate Chordates Fishes Amphibians (adult) Reptiles Birds Respiration Gills and diffusion Gills/air sacs Simple lungs and skin Lungs Lungs (tubes Lungs and air sacs; (alveoli) one-way flow) Circulation No true chambers Single loop; 2 Double loop; chambers 3 chambers Double loop; 3 chambers Double loop; 4 chambers Double loop; 4 chambers Excretion Gills and gill slits Kidney and gills Kidney Kidney Kidney Response Simple; mass Cephalization; Cephalization; Cephalization; Cephalization; Cephalization; of nerve cells small small small large large cerebrum cerebrum cerebrum cerebrum cerebrum Kidney and gills Mammals Comparing Functions of Chordates Fishes Amphibians Amphibians (adult) (adult) Reptiles Birds Mammals Muscles on either side of backbone Limbs stick out sideways; muscles and ligaments Limbs point directly toward ground; muscles and ligaments Upper limbs are wings; 2 feet; muscles and ligaments 2 or 4 legs; walk with legs straight under them; muscles and ligaments Reproduction External fertilization External fertilization External fertilization Internal fertilization; shelled egg Internal fertilization; shelled egg Internal fertilization and development Temperature Ectothermic Control Ectothermic Ectothermic Ectothermic Endothermic Endothermic Function Movement Nonvertebrate Chordates Muscles, no bones Form and Function in Vertebrates Fish Habitat Type of circulatory pathway Number of heart chambers Structures for gas exchange Excretory structures Nitrogenous waste extreted Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals water Juveniles - water Adults - land and water Land Land (air) Land, water single-loop double-loop double-loop double-loop double-loop 2 3 3 or 4 4 4 lungs lungs lungs kidneys kidneys kidneys uric acid uric acid urea gills, swim bladder gills ammonia gills (juvenile), skin, lungs, lining of mouth (adult) gills (juvenile), kidneys (adult) ammonia (juvenile), urea (adult) Questions 1. What relationship exists between the type of circulatory pathway and the number of heart chambers? Organisms with a 2-chambered heart have a single-loop and organisms with 3 or 4 – chambered hearts have a double-loop 2. What is the relationship between the habitat of an organism and the structures used for gas exchange? Aquatic organisms use gills and terrestrial organisms use lungs. 3. How does each type of nitrogenous waste excreted relate to the type of excretory structure in each group. Ammonia is excreted by organisms that use gills; uric acid and urea is excreted by organisms that use kidneys Reproduction Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals water Juveniles - water Adults - land and water Land Land (air) Land, water Type of fertilization external external internal internal internal Type of development external external internal and external external internal many many few few few Habitat Number of eggs produced Questions 4. What relationship exists between an organism’s habitat and its method of fertilization? In water, fertilization is external. On land, fertilization is internal. 5. How does the number of eggs produced relate to the method of fertilization? External fertilization requires many eggs, while internal fertilization produces fewer eggs. 6. The type of fertilization and the number of eggs produced often indicate the amount of parental care of the offspring. Use the table to predict the amount of parental care given by each vertebrate group. Fish and amphibians – little to no parental care. Reptiles – some parental care. Birds and mammals – much parental care. Esophagus Stomach Intestine Liver Gallbladder Pancreas Cloaca Crop Gizzard Cecum Rectum Shark Salamander Lizard Pigeon Cow Nostrils, mouth, and throat Trachea Lung Air sac Salamander Lizard Primate Pigeon Single-Loop Circulatory System FISHES Double-Loop Circulatory System MOST REPTILES Section 31-1 Liver Kidney Heart Cloaca Bladder Lung Digestive tract To body To lungs Right atrium From lungs Left atrium From body Ventricle Incomplete division Domestic pigeon Right atrium Heart Right ventricle Left atrium Left ventricle Complete division Section 32-1 Left atrium Right atrium Right ventricle Left ventricle Complete division