Ch.33 - Jamestown School District
advertisement

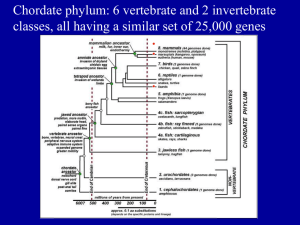
Unit 9 Chordates Ch. 33 Comparing Chordates The Chordate Family Tree The chordate family tree has its roots in ancestors that vertebrates share with tunicates & lancelets The Chordate Family Tree Evolutionary Trends in Vertebrates Over the course of evolution, the appearance of new adaptations (jaws & paired appendages) has launched adaptive radiations in chordate groups Adaptive radiation - the rapid diversification of species as they adapt to new conditions Evolutionary Trends in Vertebrates A rapid increase in the # & diversity of land vertebrates followed the evolution of 4 limbs Chordate Diversity Body Temperature & Homeostasis The control of body temperature is important for maintaining homeostasis in vertebrates, particularly in habitats where temperature varies widely with time of day & with season Body Temperature & Homeostasis The internal control of body temperature allows emperor penguins to live in cold Antarctic climates, where their feathers act as insulation Body Temperature & Homeostasis Ectotherm - the body temperature is determined by the temperature of the environ.; the animals pick up heat from, or lose heat to, their environ. Most reptiles, fishes, & amphibians are ectotherms Body Temperature & Homeostasis Endotherm - an animal whose body temp. is controlled from within; they can generate & retain heat inside their bodies Birds & mammals are endotherms Form & Function in Chordates Feeding: The blunt, broad jaws & numerous teeth of crocodiles help them catch large prey, even in thick vegetation Form & Function in Chordates Feeding: The digestive system of vertebrates have organs that are well adapted for different feeding habits Form & Function in Chordates Respiration: As a general rule, aquatic chordates (tunicates, fishes, & amphibian larvae) use gills for respiration Land vertebrates (adult amphibians, reptiles, birds, & mammals) use lungs Form & Function in Chordates Circulation: During chordate evolution, the heart developed chambers & partitions that help separate oxygen-rich & oxygen-poor blood traveling in the circulatory system The heart of fishes have 2 chambers, amphibians & most reptiles have 3 chambers, & crocodilians, birds, & mammals have 4 chambers Form & Function in Chordates Form & Function in Chordates Response: Nonvertebrate chordates have a simple nervous system with a mass of nerve cells that form a brain Vertebrates have a more complex brain with distinct regions, each with a different function Form & Function in Chordates Form & Function in Chordates Movement: The skeletal & muscular systems support a vertebrate’s body & make it possible to control movement Muscles & ligaments attach the appendages to the backbone & help control movement Form & Function in Chordates Reproduction: Almost all chordates reproduce sexually Vertebrate evolution shows a trend from external to internal fertilization