Machinability and Chip Formation
advertisement

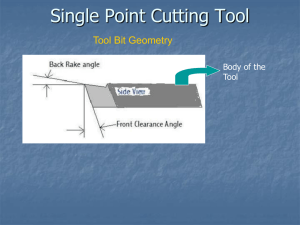
Chip Formation Machinability relative difficulty of a machine operation with regard to tool life, surface finish, and power consumption generally softer materials easier to machine Metal does NOT split off ahead of cutter as in wood Metal is sheared off at SHEAR PLANE metal is forced ahead of tool Surface finish affected by: speeds feeds depth of cut tool shape use of cutting fluid rigidity of the setup Optimum chip for operator safety is figure “9” Chip breaker curls chip to break it off keep from tangling in machine safer 3 basic types of chip formation 1. Continuous chip Continuous chip characteristics better surface finish soft or medium hardness materials that are ductile low coefficient of friction - pass across top of well polished tool chips curl or are straight and stringy chip breaker used to break the chip 2. Discontinuous chip (segmented) Discontinuous chip characteristics materials that fracture easily (cast iron) fails or breaks after only a small amount of deformation no chip breaker required chips are cleaned up easily 3. Continuous chip (with built up edge on tool) Continuous chip (built of edge) characteristics soft materials - high coef of friction stick to top of entering edge of tool caused by heat and pressure of cutting action material temporarily welds to tip of cutting tool then releases rougher surface finish tool life shortened Solutions for built up edge • • • • • no single solution change tool geometry use chip breaker cutting fluids best combination of speeds and feeds Cutting tool geometry positive rake neutral rake negative rake Positive rake tools Positive rake tool characteristics freer cutting at low speeds pos rake tools, cutting fluids, and higher speeds decrease tendency for built up edge - however, large pos rake = continuous chip Negative rake tools Negative rake tool characteristics surface disrupted more require more power stronger and have longer working life than positive low cutting speeds = poor surface finish high cutting speeds = good surface finish Most carbide tools have negative rake because: indexable insert can be turned over withstands more cutting pressure higher cutting speeds used