Climate Zones
advertisement
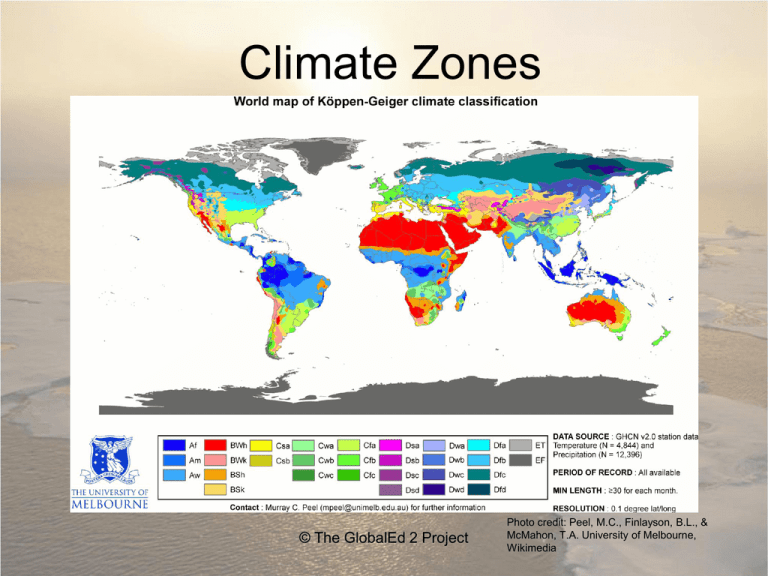
Climate Zones © The GlobalEd 2 Project Photo credit: Peel, M.C., Finlayson, B.L., & McMahon, T.A. University of Melbourne, Wikimedia Essential Questions 1. What are climate zones? 2. How are climate zones useful? © The GlobalEd 2 Project Enduring Understandings 1. One definition of time zones is that they are a series of zones that represent different climatic conditions in the United States and Canada, based on temperature. 2. Climate zones are useful to horticulturists for rating the hardiness of plants. © The GlobalEd 2 Project Types of Climate Zones 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The polar zone (E) The dry zone (B) The humid tropical zone (A) Moist-mid latitude (mild winters) zone (C) Moist-mid latitude (severe winters) zone (D) Source: http://www.csun.edu/~psk17793/ES9CP/ES9%20climate_zones.htm © The GlobalEd 2 Project E:The Polar Zone: Sub-climates • Tundra (always cold & dry with short cold summers) • Ice-cap (freezing temperatures all year) • Highland (temperatures vary widely with latitude, elevation and direction of exposed areas © The GlobalEd 2 Project B:The Dry Zone: Sub-climates • Desert (< 10 inches of rain per year with hot days. Large temperature fluctuations between day and night). • Semiarid (slightly more than 10 inches/year) © The GlobalEd 2 Project A:The Humid-Tropical Zone: Sub-climates • Tropical wet (hot & rainy throughout the year) • Tropical wet & dry (hot with wet & dry seasons) © The GlobalEd 2 Project C:Moist-mid latitude: Sub-climates • Humid subtropical (hot humid summers and mild winters) • Marine west coast (mild and rainy all year) • Mediterranean (hot & dry summers and mild winters) © The GlobalEd 2 Project D: Moist-mid latitude: Sub-climates • Humid continental (warm summers and cold snowy winters) © The GlobalEd 2 Project How are Climate Zones Useful? • Knowledge of climate zones, helps horticulturists when selecting a particular plant to farm. © The GlobalEd 2 Project