Fecal-oral Transmission Disease
advertisement
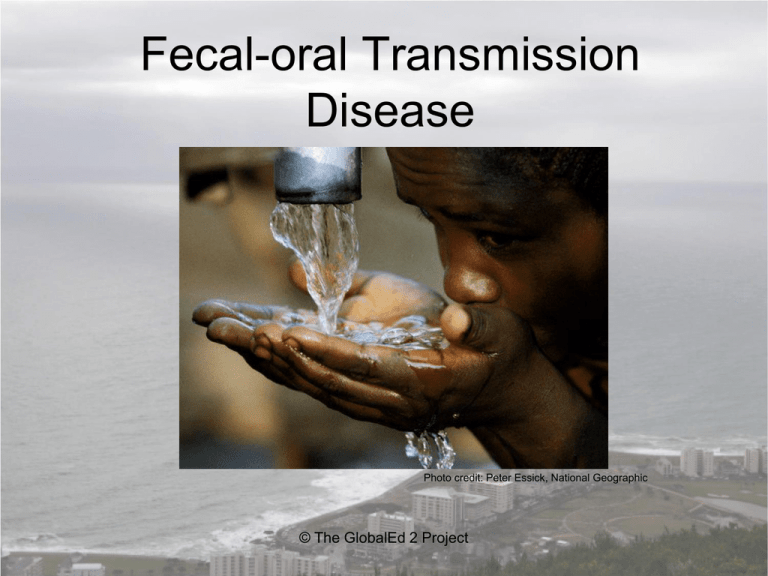
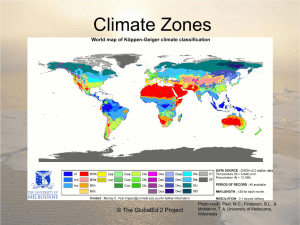
Fecal-oral Transmission Disease Photo credit: Peter Essick, National Geographic © The GlobalEd 2 Project What is Fecal-oral Transmission Disease (FOTD)? • Fecal-oral transmission disease occurs when bacteria or viruses found in the stool of one child (or animal) are swallowed by another child. © The GlobalEd 2 Project How is the Disease Contracted? • Ingesting infected foods or beverages • Swimming pools and water parks. If the water is not visibly contaminated and is adequately chlorinated, just getting the water in the mouth is usually not enough to cause an infection; the risk is greatly increased by swallowing. © The GlobalEd 2 Project How is the Disease Contracted? • Diseases can be found in feces. Food and water can become contaminated by feces. Ingestion of contaminated food and water can lead to illness. © The GlobalEd 2 Project Common Infections Spread by FOTD: • • • • • • • • E.Coli Infections Hepatitis A virus Polio Pinworms Salmonella Tapeworms Shigella Rotavirus © The GlobalEd 2 Project How Can FOTD be Prevented? • • • • Frequent hand-washing Frequent use of hand sanitizers Safe food-handling procedures Teach children to never swallow water in pools or play areas • Properly dispose of soiled baby diapers • Don’t place diaper changing stations near food preparation areas © The GlobalEd 2 Project Sources: • http://health.utah.gov/opha/publications/hs u/08May_EntericDis.pdf • http://www.drgreene.com/azguide/fecaloral-transmission • http://www.wordiq.com/definition/Transmis sion_%28medicine%29 © The GlobalEd 2 Project