Vacuum science
advertisement

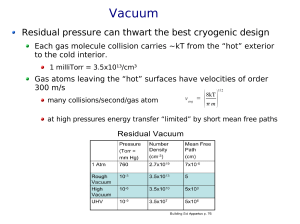
Vacuum science Outline • Kinetic theory of gases • Performance measures • Vacuum pumps – Positive displacement – Momentum transfer – Entrainment • Pressure measurement Kinetic theory of gases Maxwell speed distribution: Average magnitude of velocity: Root mean square velocity: Mean free path • The average distance a gas molecule travels before colliding with another gas molecule or the container walls • Let be the particle diameter. • Then will be the cross-sectional area for hardsphere collisions, and the mean free path: Gas flow • Viscous flow – The gas behaves like a coherent coherent, collective medium – Collisions with each other are more frequent than with the walls – Occurs at pressures greater than 1 mtorr • Molecular flow – Collisions with walls are more frequent than with each other – Occurs at pressures less than 1 mtorr – Mean free path is larger than the chamber length Performance measures • Pumping speed (S) is the volumetric flow rate of a pump at its inlet, volume per unit of time • Throughput Q – Q ̴ mass flow rate at const. T – torr-L/s – Q = PS Vacuum pump pressure ranges Vacuum pumps • Positive displacement (rough vacuum) – Mechanical – 3 steps: capture a volume of gas, compression of the captured volume, and gas expulsion • Momentum transfer (high vacuum) – Knock gas molecules out of the chamber • High speed jets of dense fluid • High speed rotating blades • Entrainment (to and including ultrahigh vacuum) – Capture gases in a solid or adsorbed state Positive displacement • A simple piston pump Positive displacement Rotary vane pump Roots blower pump Momentum transfer Diffusion pump Turbomolecular pump Entrainment Ultrahigh vacuum • Titanium sublimation pump – Chemisorption or gettering of active gases – Deposit a thin film of highly reactive metal on the inside surface of the pump by heating a titaniumcontaining filament • Sputter-ion pump – Chemisorption and burying • On impact the accelerated ions will typically bury themselves in the cathode as well as sputter some of the cathode • Also pumps noble gases by burying Pressure measurement Capacitance manometer • Mechanical • Depends on a pressure difference between the chamber to be measured and a reference volume • Detects the movement of a thin metal diaphragm • For rough vacuum - difficult to measure below 1 mtorr Pressure measurement Thermal conductivity • Measures the thermal conductivity of the gas • Operate by passing a current through a wire and measure its tempreature • For rough vacuum - above 1 mtorr Pressure measurement Ionization • For high and ultrahigh vacuum • An electron stream ionize the gas in the gauge which again are collected by an electrical field • This ion current is a function of the chamber pressure • Hot cathode (filament) torr down to torr • Cold cathode (plasma) torr down to torr