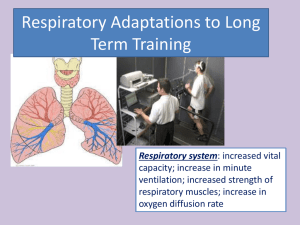
the respiratory system: mechanics of ventilation
advertisement
RESPIRATION II THE HUMAN ORGANISM ANNOUNCEMENTS • Exam 3 is Monday, Dec. 14th • Practice Exam will be posted next week • Office hours TBA • Final Exam is Wednesday, Dec 16th • Same format as hourly exams • Cumulative • May NOT be dropped • No Practice Final • Study material from previous exams THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: MECHANICS OF VENTILATION Ventilation is the Result of: • Behavior of Gases • Gas laws explain movement of gases in respiratory system • Mechanical events • Muscle contraction and relaxation Behavior of Gases: • Atmosphere is composed of a mix of gases: • The presence of a gas in mixture is expressed as partial pressure (Px) GAS BEHAVIOR Dalton’s Law: GAS BEHAVIOR GAS BEHAVIOR Boyle’s Law: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: MECHANICS OF VENTILATION • Atmospheric Pressure (ATM): • Intrapulmonary Pressure: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: MECHANICS OF VENTILATION Mechanics of Ventilation: • Lungs stuck to thoracic cavity wall • When thoracic cavity expands or recoils, so do lungs MECHANICS OF VENTILATION INHALATION: MECHANICS OF VENTILATION EXHALATION: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: MECHANICS OF VENTILATION RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: AIR FLOW IN LUNGS Factors Effecting Air Flow: – Pressure gradients – Resistance to flow (which is influenced by:) » Length of airways (constant) » Viscosity of air (constant) THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: AIR FLOW IN LUNGS Factors Effecting Air Flow: • Trachea and Bronchi: – Rigid structures – Approx. 90% of airway resistance – Constant sources of resistance Factors Effecting Air Flow: • Bronchioles: – Approx. 10% of resistance – Source of variable resistance since airways don’t have fixed diameter THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: AIR FLOW IN LUNGS