Greenhouse-science - San Jose State University
advertisement

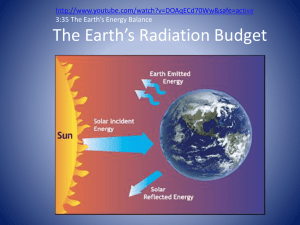
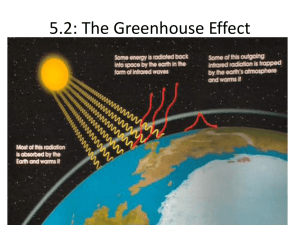
BAESI - Global Warming: Food Climate Connections The Greenhouse Effect Dr. Eugene Cordero San Jose State University Outline Greenhouse effect Energy Balance Activities 1 The Atmosphere Principal Atmospheric Gases GAS MASS Nitrogen 75% Oxygen 23% Argon 1% Water Vapor 0.3% CO2 0.06% Principal Atmospheric Gases GAS MASS Nitrogen 75% Oxygen 23% Argon 1% Water Vapor 0.3% CO2 0.06% Greenhouse gases Earth’s Energy Balance Energy entering top of atmosphere = Energy leaving top of atmosphere Energy entering the Earth’s surface = Energy leaving Earth’s surface Solar Radiation (Sunlight) Sunlight is primarily made up of the following: – Visible Light (44%) – Infrared Radiation (48%) – Ultraviolet Radiation (7%) Unit: 1 m = 0.000001 m Energy from the Sun Obviously, the Sun provides the Earth with it’s energy. The question is, how much of the Sun’s energy does the Earth get? Sun’s energy is either – Scattered (reflected away) or – Absorbed Scattering happens by bouncing off – Particles in the atmosphere – Earth’s surface Absorption happens when certain gases absorb the energy – The reality is the only certain gases absorb certain wavelengths. Incoming solar radiation Each ‘beam’ of incoming sunlight can be either: – Reflected back to space: Albedo Clouds Atmosphere Surface – Or absorbed; either by atmosphere (e.g. clouds or ozone) or Earth’s surface. Absorption of radiation Absorption of shortwave radiation by atmospheric gas molecules is fairly weak; – most absorption of shortwave radiation occurs at the Earth’s surface. Most gases do not interact strongly with longwave radiation, however – Greenhouse gas molecules absorb certain wavelengths of longwave radiation. Absorption of radiation in the Earth’s atmosphere Some surface radiation escapes to space Most outgoing longwave is absorbed in atmosphere (by greenhouse gases) Longwave radiation is emitted from surface. Some atmospheric radiation escapes to space Greenhouse gases emit longwave upward and downward Some atmospheric radiation is absorbed at the surface Greenhouse Effect Sequence of steps: 1. Solar radiation absorbed by earth’s surface. 2. Earth gives off infrared radiation. 3. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the Earth’s infrared radiation. 4. Greenhouse gases (water and CO2) give off infrared radiation in all directions. 5. Earth absorbs downward directed infrared radiation Result: warmer surface temperature Earth’s Greenhouse Effect Without the greenhouse effect, the surface temperature of Earth would be – Very Cold (-18°C) Greenhouse gases play an important role in shaping climate. – More GHGs – warmer climate – Less GHGs – cooler climate Activity Draw a diagram showing how the earth is heated by the Sun. Include arrows and/or lines to indicate the ‘Energy Balance” of the earth. Energy Balance – Energy coming in and energy going out. In your diagram, include how clouds absorb, reflect and emit energy. Activity 2 1. What percentage of the sun’s radiation is a) absorbed by the Earth’s surface? b) absorbed by the atmosphere c) reflected out to space? 2. What percentage of the energy received by the earth’s surface comes directly from greenhouse gas emissions? 3. If the sun’s radiation was to increase by 10%, how would the following energy units change (increase, decrease or stay the same) a) Energy gained by the Earth’s surface. b) Energy lost by the Earth’s surface. c) Energy emitted by greenhouse gases. d) Energy lost to space.