Global shortwave radiation cascade (source Pidwirney online)
advertisement
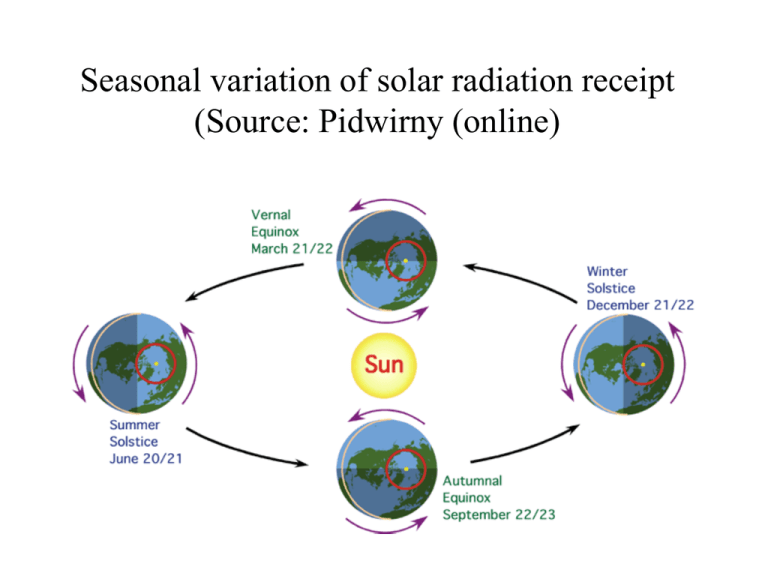
Seasonal variation of solar radiation receipt (Source: Pidwirny (online) Please consult Pidwirny Fundamentals of Physical Geography @ http://www.physicalgeography.net/fundamentals/contents.html and answer the following questions • How has the sun’s output of energy changed over the last 3.5 billion years? (5d) • How has the Earth’s temperature changed over its history? (5d)) • What is the present temperature of the sun? (6d) • The sun emits most of its radiation through what wavelength band? (6f) Day length Solar radiation received Source: Pidwirny (online) Helions Source: Pidwirny (online ) What is solar energy received at the Earth’s surface used for? • Heating the earth’s surface and lower atmosphere • Melting ice and evaporating water • Photosynthesis in plants Global shortwave radiation cascade (source Pidwirney online) Radiation from Sun 100 units Albedo 30 Reflected by Clouds 20 clouds Stratospheric Absorption 2 Tropospheric absorption 17 Scattered 6 Direct 28 Surface reflection 4 Diffused 23 Energy absorbed by Earth’s surface Annual (1987) reflectivity of the Earth's surface Source: Pidwirney online •Albedo of the Earth’s surface •Dry sand 35 to 45 % •Broadleaf deciduous forest 5 to 10 % •Needleleaf coniferous forest 10 to 20 % •Grass type vegetation 15 to 25 % •Fresh snow 90% Global longwave radiation cascade (source Pidwirney online) Surface longwave emmission lost to 6 space Atmospheric absorption of surface emission 111 Surface longwave emission 117 Atmospheric longwave emmission lost to space 64 Emission by atmosphere and clouds 160 Atmospheric longwave emission to Earth 96 Latent heat 23 evaporation Energy released by Earth’s surface Sensible heat 7 Conduction & convection The annual pattern of solar radiation absorption at the Earth's surface for the year 1987 Source: Pidwirney online Redistribution of global energy - winds • Energy absorption Heating of the Earth’s surface Heating of the atmosphere Development of pressure cells Development of wind systems Lower atmosphere wind systems Upper atmosphere wind systems Lower atmosphere Upper atmosphere Atmospheric circulation Upper atmosphere Ocean currents Subsurface currents Red is near subsurface currents Blue is lower cold currents











