the galvanic skin resistance
advertisement

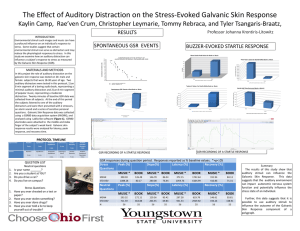
Galvanic skin response & The polygraph 2010. 05. 26. Ji-Won Kim Galvanic skin response GSR Referred to as the galvanic skin resistance varies in accordance with the emotional state of the subject Feeble electric current is applied between two electrode GSP Referred to as the galvanic skin potential varies in accordance with the emotional state of the subject Two electrode is connected to a suitable voltage amplifier GSR의 원리 A change in autonomic tone (Sympathic nerve system), occuring in the skin and subcutaneous tissue Sweating and cutaneous blood flow GSR의 원리 The increase in sweat lowers the electrical resistance of the skin Sweat contain water and electrolyte Water and electrolyte increase electrical conductivity of the skin Various application of GSR 거짓말 탐지기 감성마켓팅 1 2 Various application of GSR Sports Polygraph Literal meaning Many measures Poly-many, Graph-write Be combined with the detection and recording of other autonomicdependent psychophysiological variables Heart rate, respiratory rate and blood pressure Experimental objectives Record the GSR Observe and record changes in respiratory rate, heart rate and skin resistance Associated with somatic and special sensory stimuli Associated with cognitive behavior and emotion Analyze a 3-channel polygram recorded under various experimental conditions ELECTROOCULOGRAM (EOG) Visual fixation Visual fixation One of the most important function the eye Two primary mechanisms Voluntary fixation mechanism Fixation on another person from across a crowded room Involuntary fixation mechanism Involuntary movements Tremor 30-80Hz (cycles/sec) Slow drifts Drifting movements of the eyes Flicking movements The image is once again projected onto the fovea Tracking movements and saccades Tracking movements When you wish to follow a moving object Smooth motion and tracking an object in your visual field Saccades When you read or when objects are streaming past you Eye jumps from point to point A rate of about three jumps per second EOG(electrooculogram) Eye movement can be recorded as an electrooculogram Recording of changes in voltage that occur with eye position Eye is a spherical “battery” Positive: front at the cornea Negative: behind at the retina Potential: about 0.4~1.0mV Up to ±70° EOG(electrooculogram) EOG(electrooculogram) Experimental objectives Fixated on a stationary object vs. tracking objects Measure duration of saccades and fixation during reading Record spatial position of eye movements Thank you Question?