The Effect of Auditory Distraction on the Stress-Evoked Galvanic Skin... Kaylin Camp, Rae’ven Crum, Christopher Leymarie, Tommy Rebraca, and... BUZZER-EVOKED STARTLE RESPONSE
advertisement
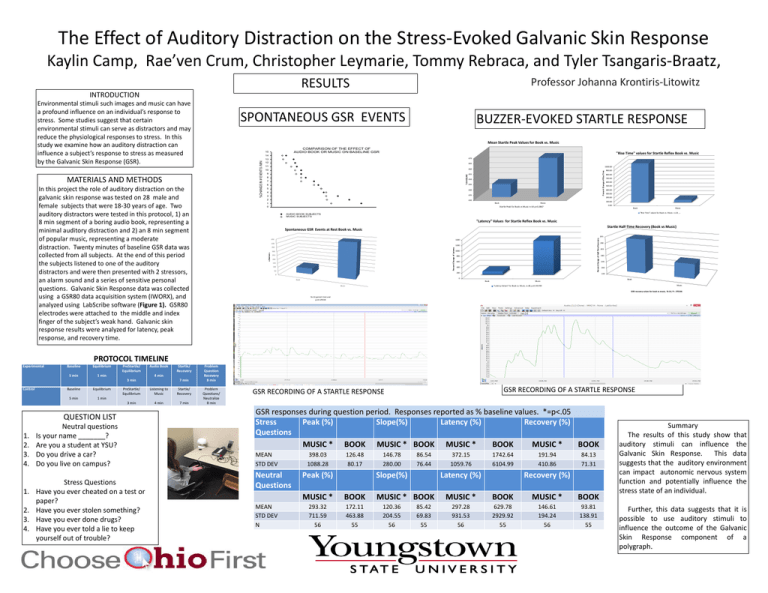
The Effect of Auditory Distraction on the Stress-Evoked Galvanic Skin Response Kaylin Camp, Rae’ven Crum, Christopher Leymarie, Tommy Rebraca, and Tyler Tsangaris-Braatz, RESULTS Professor Johanna Krontiris-Litowitz INTRODUCTION Environmental stimuli such images and music can have a profound influence on an individual’s response to stress. Some studies suggest that certain environmental stimuli can serve as distractors and may reduce the physiological responses to stress. In this study we examine how an auditory distraction can influence a subject’s response to stress as measured by the Galvanic Skin Response (GSR). SPONTANEOUS GSR EVENTS BUZZER-EVOKED STARTLE RESPONSE Mean Startle Peak Values for Book vs. Music COMPARISON OF THE EFFECT OF AUDIO BOOK OR MUSIC ON BASELINE GSR 15 "Rise Time" values for Startle Reflex Book vs. Music In this project the role of auditory distraction on the galvanic skin response was tested on 28 male and female subjects that were 18-30 years of age. Two auditory distractors were tested in this protocol, 1) an 8 min segment of a boring audio book, representing a minimal auditory distraction and 2) an 8 min segment of popular music, representing a moderate distraction. Twenty minutes of baseline GSR data was collected from all subjects. At the end of this period the subjects listened to one of the auditory distractors and were then presented with 2 stressors, an alarm sound and a series of sensitive personal questions. Galvanic Skin Response data was collected using a GSR80 data acquisition system (IWORX), and analyzed using LabScribe software (Figure 1). GSR80 electrodes were attached to the middle and index finger of the subject’s weak hand. Galvanic skin response results were analyzed for latency, peak response, and recovery time. 470 12 465 11 1000.00 10 460 9 455 8 7 6 5 Percent Change of Rise TIme MATERIALS AND METHODS 13 % BASELINE %CHANGE IN # EVENTS /MIN 14 450 445 440 4 3 435 2 430 900.00 800.00 700.00 600.00 500.00 400.00 300.00 200.00 1 Book 0 100.00 Music 0.00 Startle Peak for Book vs Music n=14 p=0.2867 Book Music "Rise Time" values for Book vs. Music. n=14 ,… AUDIO BOOK SUBJECTS MUSIC SUBJECTS "Latency" Values for Startle Reflex Book vs. Music Startle Half-Time Recovery (Book vs Music) Spontaneous GSR Events at Rest Book vs. Music 1400 400 1200 Percent Change of Latency 350 300 uSiemens Percent Change of Half-Time Recovery 255 450 250 200 150 100 50 1000 800 600 400 200 0 Book Music 245 240 235 230 225 0 Book 250 Book Music Music "Latency Values" for Book vs. Music, n=28, p=0.191709 GSR recovery values for book vs music, N=14, P= .370146 N=14 paired t-test and p=0.129158 PROTOCOL TIMELINE Experimental Baseline Equilibrium 5 min 1 min Baseline Equilibrium 5 min 1 min PreStartle/ Equilibrium Audio Book 3 min Control 1. 2. 3. 4. 7 min PreStartle/ Equilibrium Listening to Music Startle/ Recovery 3 min 4 min 7 min QUESTION LIST 1. 2. 3. 4. Startle/ Recovery 4 min Neutral questions Is your name _______? Are you a student at YSU? Do you drive a car? Do you live on campus? Stress Questions Have you ever cheated on a test or paper? Have you ever stolen something? Have you ever done drugs? Have you ever told a lie to keep yourself out of trouble? Problem Question Recovery 8 min Problem Questions/ Neutralize 8 min GSR RECORDING OF A STARTLE RESPONSE GSR RECORDING OF A STARTLE RESPONSE GSR responses during question period. Responses reported as % baseline values. *=p<.05 Stress Peak (%) Slope(%) Latency (%) Recovery (%) Questions MUSIC * BOOK MUSIC * BOOK MUSIC * BOOK MUSIC * BOOK MEAN STD DEV N Neutral Questions MEAN STD DEV N 398.03 1088.28 126.48 80.17 146.78 280.00 86.54 76.44 372.15 1059.76 1742.64 6104.99 191.94 410.86 84.13 71.31 56(%) Peak 55 56 Slope(%) 55 56 (%) Latency 55 56 (%) Recovery 55 MUSIC * BOOK MUSIC * BOOK MUSIC * BOOK 293.32 711.59 56 172.11 463.88 55 297.28 931.53 56 629.78 2929.92 55 146.61 194.24 56 93.81 138.91 55 MUSIC * BOOK 120.36 204.55 56 85.42 69.83 55 Summary The results of this study show that auditory stimuli can influence the Galvanic Skin Response. This data suggests that the auditory environment can impact autonomic nervous system function and potentially influence the stress state of an individual. Further, this data suggests that it is possible to use auditory stimuli to influence the outcome of the Galvanic Skin Response component of a polygraph.